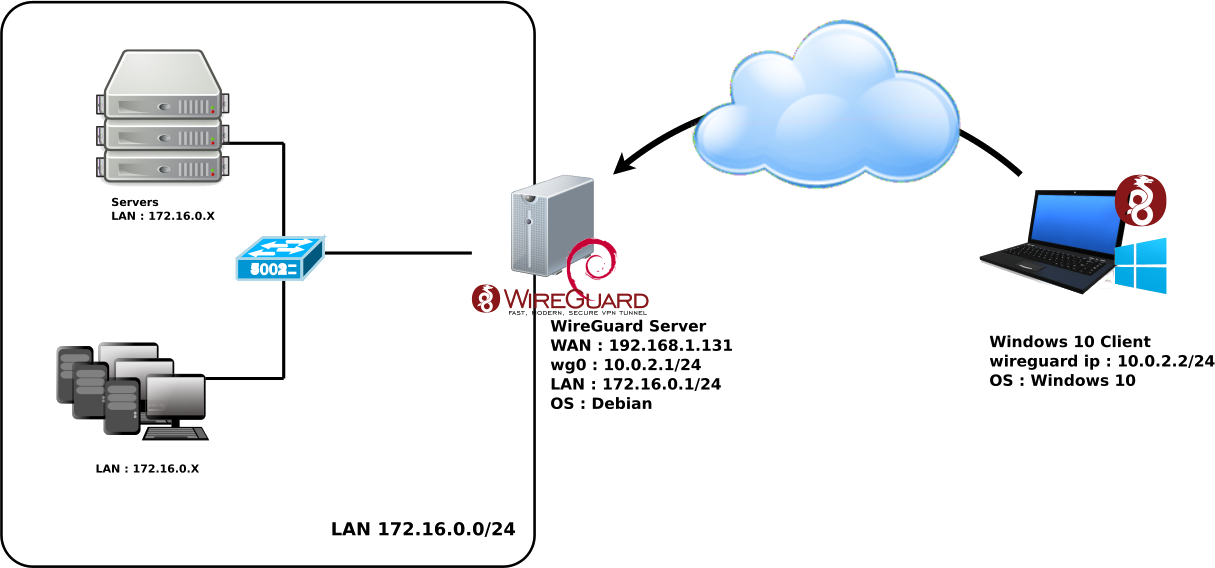
WireGuard est le nouveau VPN à la mode. Il est performant, sécurisé et facile à configurer.
Voyons comment le mettre en place dans un environnement Debian GNU/Linux serveur avec des clients Windows.
root@host:~# apt update
root@host:~# apt install wireguard
root@host:~# cd /etc/wireguard/
root@host:~# umask 077
root@host:~# wg genkey > wg-private.key
root@host:~# wg pubkey < wg-private.key > wg-public.key
root@host:~# cat wg-private.key
2GIURzIDBgI1Y+1Ei+i2C5kEOR53mH172MaidaVpD3M=
# define the WireGuard service
[Interface]
# contents of file wg-private.key that was recently created
PrivateKey = 2GIURzIDBgI1Y+1Ei+i2C5kEOR53mH172MaidaVpD3M=
# UDP service port; 51820 is a common choice for WireGuard
ListenPort = 51820
# indicate that wg0 should be created when the system boots, and on ifup -a
auto wg0
# describe wg0 as an IPv4 interface with static address
iface wg0 inet static
# static IP address
address 10.0.2.1/24
# before ifup, create the device with this ip link command
pre-up ip link add $IFACE type wireguard
# before ifup, set the WireGuard config from earlier
pre-up wg setconf $IFACE /etc/wireguard/$IFACE.conf
# after ifdown, destroy the wg0 interface
post-down ip link del $IFACE
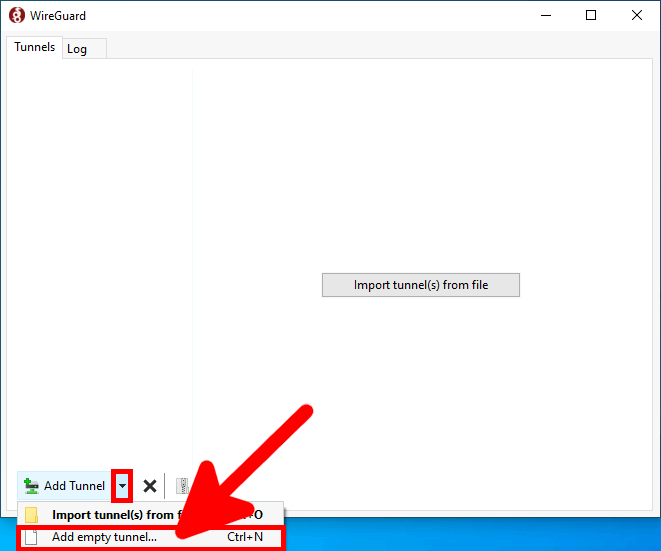
Télécharger la dernière version du logiciel sur le site officiel https://wireguard.com/, et l'installer.

root@host:~# cat /etc/wireguard/wg-public.key hlKy6azGCB0uVbCdkW8Htx23k57iWzOFJRLAYHTx5wU=
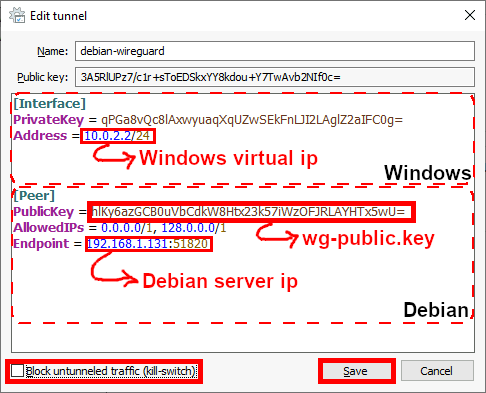
[Interface] PrivateKey = qPGa8vQc8lAxwyuaqXqUZwSEkFnLJI2LAglZ2aIFC0g= Address = 10.0.2.2/24 [Peer] PublicKey = hlKy6azGCB0uVbCdkW8Htx23k57iWzOFJRLAYHTx5wU= AllowedIPs = 0.0.0.0/1, 128.0.0.0/1 Endpoint = 192.168.1.131:51820
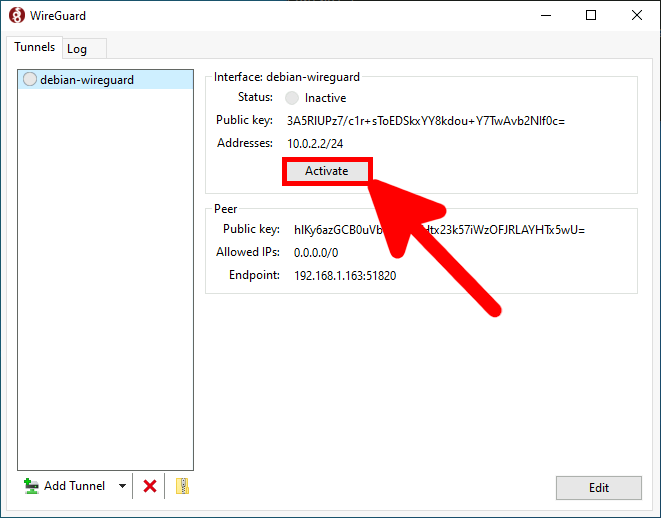
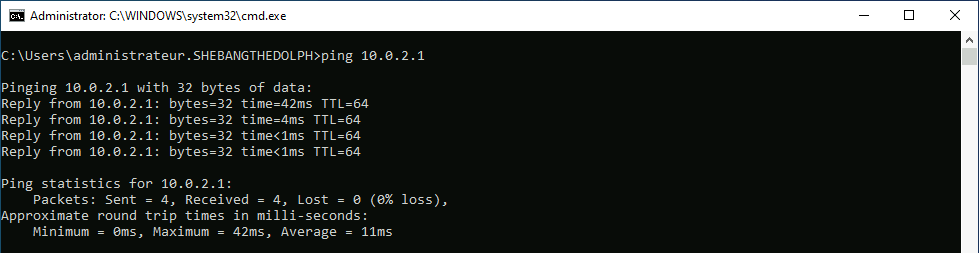
root@host:~# ifup wg0

root@host:~# wg set wg0 peer CLIENT_PUBLIC_KEY allowed-ips 0.0.0.0/0
root@host:~# wg show interface: wg0 public key: hlKy6azGCB0uVbCdkW8Htx23k57iWzOFJRLAYHTx5wU= private key: (hidden) listening port: 51820 peer: 3A5R|UPz7/c1r+sToEDSkxYY8kdou+Y7TwAvb2NIf0c= endpoint: WINDOWS_IP:52925 allowed ips: 0.0.0.0/0 latest handshake: 6 seconds ago transfer: 14.44 KiB received, 1.87 KiB sent
# indicate that wg0 should be created when the system boots, and on ifup -a
auto wg0
# describe wg0 as an IPv4 interface with static address
iface wg0 inet static
# static IP address
address 10.0.2.1/24
# before ifup, create the device with this ip link command
pre-up ip link add $IFACE type wireguard
# before ifup, set the WireGuard config from earlier
pre-up wg setconf $IFACE /etc/wireguard/$IFACE.conf
# after ifdown, destroy the wg0 interface
post-down ip link del $IFACE
# allowed clients
up wg set wg0 peer CLIENT01_PUBLIC_KEY allowed-ips 0.0.0.0/0
up wg set wg0 peer CLIENT02_PUBLIC_KEY allowed-ips 0.0.0.0/0
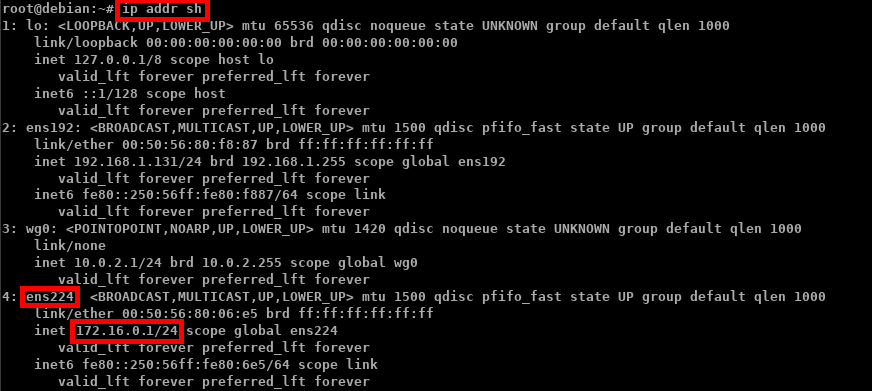
net.ipv4.ip_forward = 1
root@host:~# sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.conf
root@host:~# cat /proc/sys/net/ipv4/ip_forward 1
root@host:~# nft add table ip NAT
root@host:~# nft add chain ip NAT my_masquerade '{ type nat hook postrouting priority 100; }'
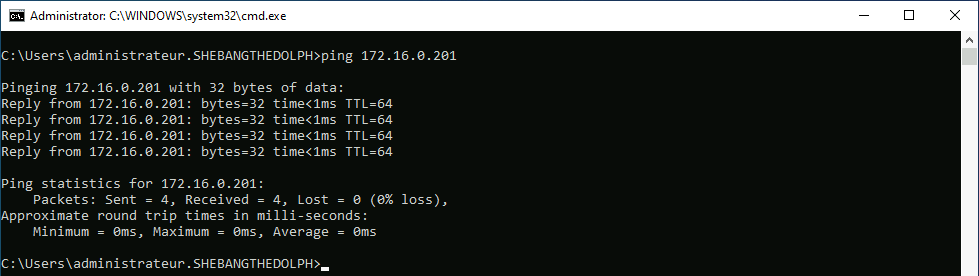
root@host:~# nft add rule NAT my_masquerade ip saddr { 10.0.2.0/24 } oifname ens224 masquerade
root@host:~# nft add rule ip filter INPUT udp dport 51820 ct state new,established counter accept
root@host:~# nft add rule ip filter OUTPUT udp sport 51820 ct state established counter accept
#!/usr/sbin/nft -f
flush ruleset
table inet filter {
chain input {
type filter hook input priority 0;
udp dport 51820 ct state new,established counter accept
}
chain forward {
type filter hook forward priority 0;
}
chain output {
type filter hook output priority 0;
udp sport 51820 ct state established counter accept
}
}
table ip NAT {
chain my_masquerade {
type nat hook postrouting priority 100; policy accept;
ip saddr { 10.0.2.0/24 } oifname "ens224" masquerade comment "outgoing NAT"
}
}
root@host:~# root@host:~# systemctl enable nftables.service
root@host:~# modprobe wireguard && echo module wireguard +p > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
root@host:~# tail -f /var/log/syslog
root@host:~# modprobe wireguard && echo module wireguard -p > /sys/kernel/debug/dynamic_debug/control
Contact :