Securely Mount Windows Shares on Debian GNU/Linux with Kerberos
- Last updated: Jun 21, 2025

In a Microsoft Windows environment, it is common to mount a network share on a GNU/Linux system using the mount command and the CIFS utility. While this method is straightforward to implement, it relies on the outdated and less secure NTLM (v1 and v2) authentication protocols, which present significant security risks due to their inherent weaknesses.
A more secure alternative is to use Kerberos authentication when mounting Windows shares from Linux. Unlike NTLM, Kerberos is a modern, robust protocol designed to provide strong authentication. Although it involves additional configuration steps, the enhanced security it offers makes it well worth the effort.
This guide walks you through the process of setting up and configuring Kerberos-based authentication, enabling you to securely access Windows shares from your GNU/Linux systems.
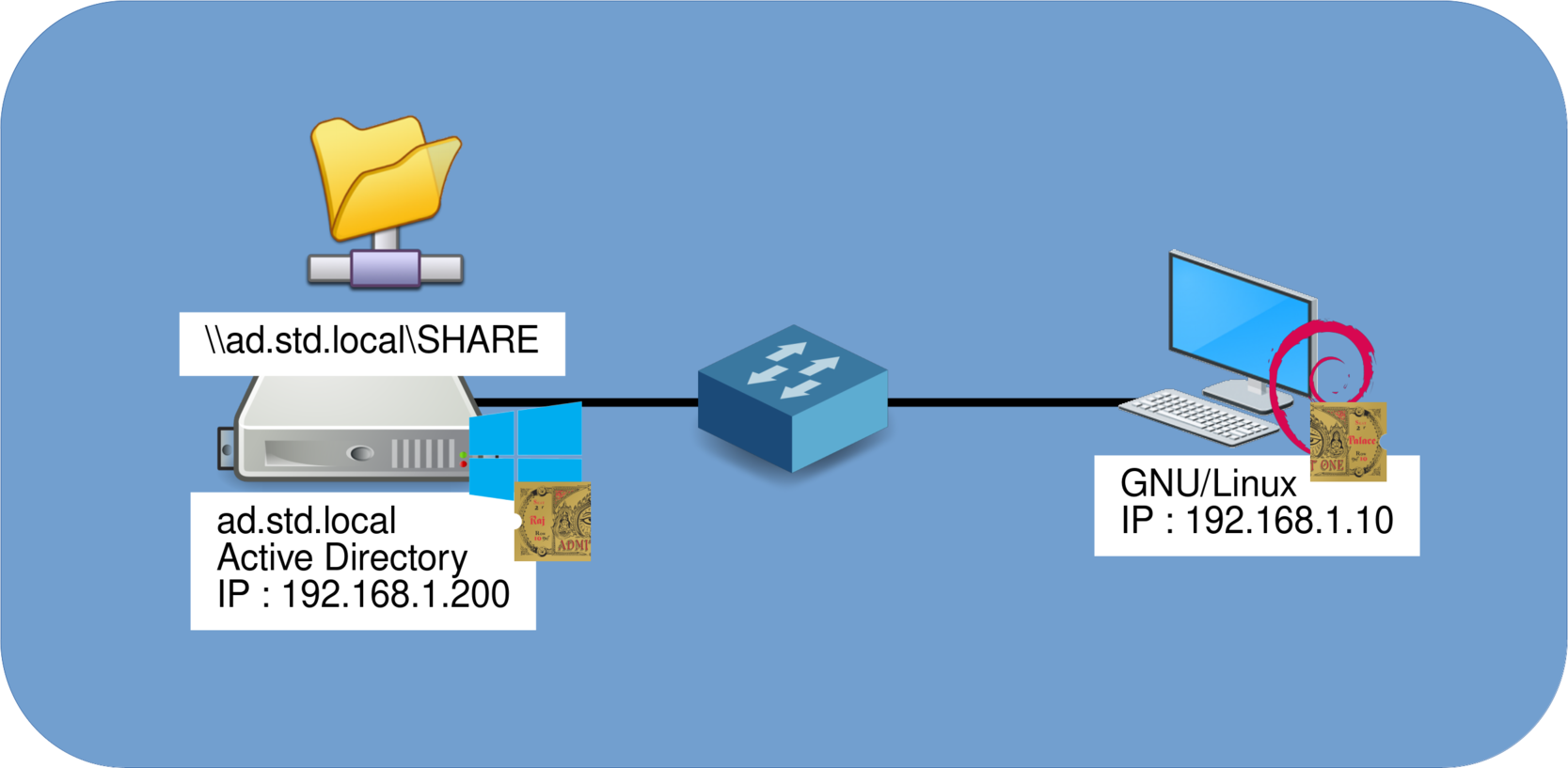
Network Architecture
- This guide is based on the following example architecture:
- A Windows domain: std.local
- A shared folder hosted on an Active Directory server, accessible via \\ad.std.local\SHARE\
- A Windows user with access permissions: j.valmer@std.local
- A GNU/Linux client running a standard Debian installation
- The share is mounted by the user john on the Debian system
Install and Configure
⚠️ Prerequisite: Ensure that both the Windows server and the Debian client are time-synchronized. Kerberos is highly sensitive to time differences. ⚠️
- Install the required packages:
root@desktop:~# apt update && apt install cifs krb5-user ntp- Configure your DNS resolver by editing
/etc/resolv.confto point to your Active Directory (AD) server:
domain std.local
search std.local
nameserver 192.168.1.200- Edit the
/etc/krb5.conffile:
[libdefaults]
default_realm = STD.LOCAL
ticket_lifetime = 1d
renew_lifetime = 7d
dns_lookup_realm = false
dns_lookup_kdc = true
[realms]
STD.LOCAL = {
kdc = ad.std.local
admin_server = ad.std.local
}Mount
Prerequisites
- Check your
UID(user ID):
john@desktop:~$ id -u
1000- Check your
GID(group ID):
john@desktop:~$ id -g
1000- Confirm your current
username:
john@desktop:~$ echo $USER
john- Create the local directory where the share will be mounted:
john@desktop:~$ sudo mkdir /mnt/win_shareClassical Mount with NTLM Authentication
- Below are common mount options for NTLM-based authentication:
domain=: Specifies the Windows domain of the user.uid=: Sets the user ID that will own all files and directories on the mounted share, if the server doesn't provide ownership info.gid=: Sets the group ID that will own all files and directories on the mounted share, if the server doesn't provide group ownership info.
john@desktop:~$ sudo mount -t cifs username=j.valmer,domain=std.local,uid=1000,gid=1000 //192.168.1.200/SHARE /mnt/win_shareMount with Kerberos Authentication
- Obtain a Kerberos ticket (note: the username is case-sensitive):
john@desktop:~$ kinit j.valmer@STD.LOCAL
Password for j.valmer@STD.LOCAL:- Verify that the Kerberos ticket was successfully obtained:
john@desktop:~$ klist
Ticket cache: FILE:/tmp/krb5cc_1000
Default principal: j.valmer@STD.LOCAL
Valid starting Expires Service principal
09/08/2023 18:19:54 10/08/2023 04:19:54 krbtgt/STD.LOCAL@STD.LOCAL
renew until 10/08/2023 18:19:50
09/08/2023 18:19:59 10/08/2023 04:19:54 cifs/ad.std.local@
renew until 10/08/2023 18:19:50
Ticket server: cifs/ad.std.local@STD.LOCAL- Understand the following mount options for Kerberos authentication:
- Use the
server name(SPN) instead of the IP address in the share path. Kerberos requires DNS resolution to match the SPN; IP addresses will not work. cruid=: Specifies the UID of the user owning the Kerberos credentials cache. Required when usingsec=krb5orkrb5i.sec=krb5i: Enables Kerberos v5 authentication with packet signing for integrity. (Usekrb5alone for authentication without signing.)
- Use the
john@desktop:~$ sudo mount -t cifs cruid=john,user=john,sec=krb5i,uid=1000,gid=1000 //ad.std.local/SHARE /mnt/win_share