Join a Debian GNU/Linux Server to an Active Directory Domain Using Winbind
- Last updated: Jun 27, 2025
This guide explains how to configure a Samba file server with Winbind on GNU/Linux to integrate it into an Active Directory environment. The goal is to allow domain users to authenticate and access shared resources seamlessly using their existing credentials.
- Key benefits of using Winbind include:
- Enables GNU/Linux systems to authenticate and access resources on Windows servers
- Maps Windows users and groups to manage ACLs on Samba shares
- Centralizes account and authentication management via Active Directory
This tutorial is based on a Debian 12 server setup.
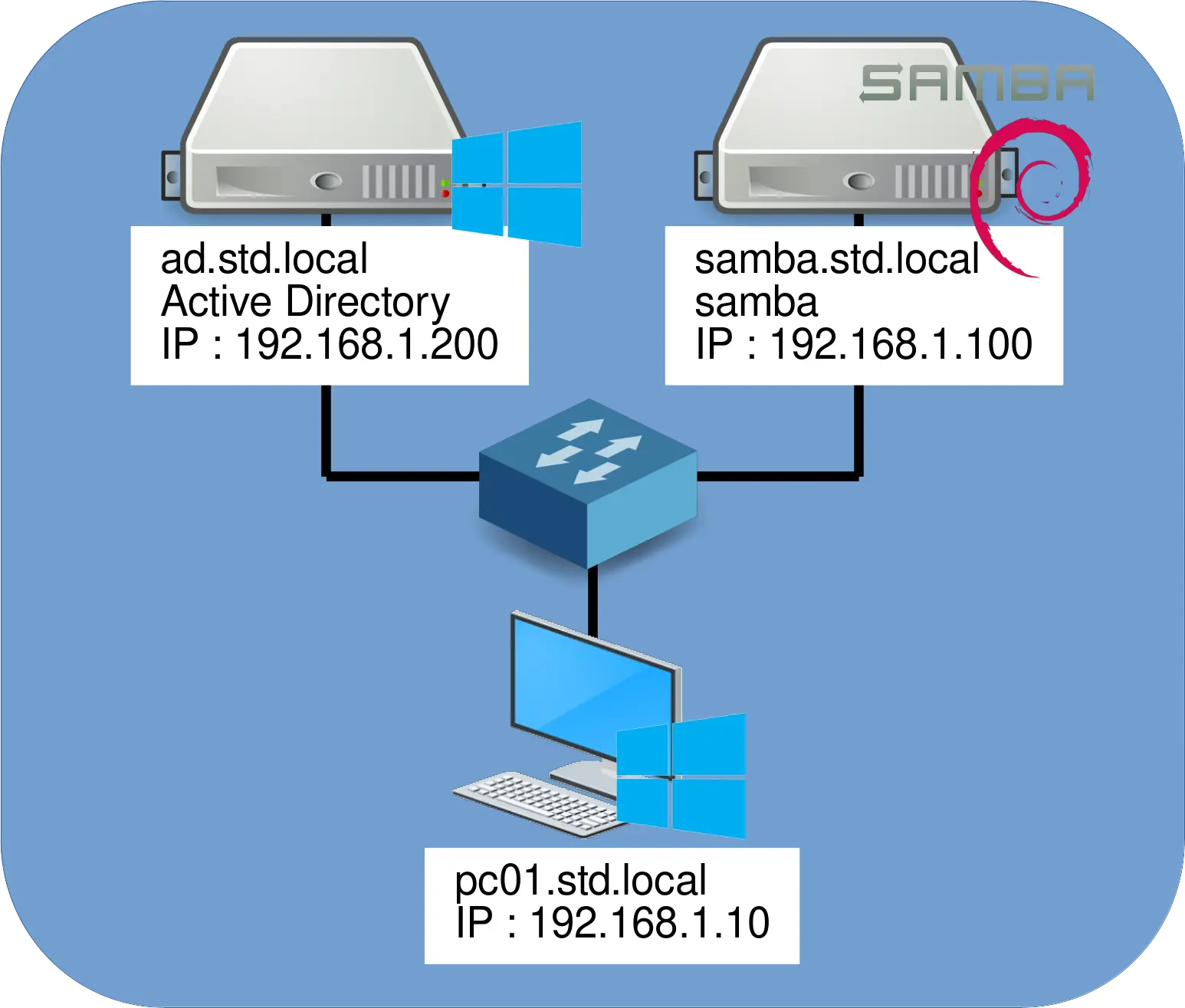
Network Architecture
Installation and Configuration
- Set the server hostname:
root@SAMBA:~# echo "SAMBA" > /etc/hostnameroot@SAMBA:~# hostname SAMBA- Edit the
/etc/hostsfile to map the hostname to its local IP:
127.0.0.1 localhost
127.0.1.1 samba.std.local samba- Edit the
/etc/resolv.conffile to configure DNS resolution:
domain std.local
search std.local
nameserver 192.168.1.200- Install the required packages for Samba, Winbind, and Kerberos support:
root@SAMBA:~# apt update && apt install samba winbind libnss-winbind libpam-winbind krb5-user- Configure Kerberos by editing the
/etc/krb5.conffile:
[libdefaults]
default_realm = STD.LOCAL
ticket_lifetime = 1d
renew_lifetime = 7d
dns_lookup_realm = false
dns_lookup_kdc = true
[realms]
STD.LOCAL = {
kdc = 192.168.1.200
admin_server = 192.168.1.200
}- Create the shared folder that will be accessible over the network:
root@SAMBA:~# mkdir /data- Edit the
/etc/samba/smb.conffile to configure the Samba server and define the share:
[global]
workgroup = std
security = ads
realm = std.local
idmap config *:backend = tdb
idmap config *:range = 700001-800000
idmap config STD:backend = rid
idmap config STD:range = 10000-700000
winbind use default domain = yes
template homedir = /home/%U
map acl inherit = yes
template shell = /bin/bash
winbind enum users = yes
winbind enum groups = yes
vfs objects = acl_xattr
; improve security :
ntlm auth = no
; improve security, Windows > 8 only :
server min protocol = SMB3_00
[share]
path = /data
writable = yes
guest ok = no
create mask = 660
directory mask = 770- Validate the Samba configuration file to ensure there are no syntax errors:
root@SAMBA:~# testparm- Edit the
/etc/nsswitch.conffile to include Winbind in user and group resolution:
# /etc/nsswitch.conf
#
# Example configuration of GNU Name Service Switch functionality.
# If you have the `glibc-doc-reference' and `info' packages installed, try:
# `info libc "Name Service Switch"' for information about this file.
passwd: files systemd winbind
group: files systemd winbind
shadow: files systemd
gshadow: files systemd
hosts: files dns
networks: files
protocols: db files
services: db files
ethers: db files
rpc: db files
netgroup: nis- Join the Debian server to the Active Directory domain:
root@SAMBA:~# net ads join -U administrator@std.local- Restart the necessary services to apply the configuration:
root@SAMBA:~# systemctl restart smbd.service nmbd.service winbind.service- Verify connectivity with the Active Directory domain using
wbinfo:
root@SAMBA:~# wbinfo --ping-dc
checking the NETLOGON for domain[STD] dc connection to "ad.std.local" succeeded- List domain users and groups using the
wbinfotool to confirm proper integration:
root@SAMBA:~# wbinfo -u
administrator
guest
krbtgt
e.cartman
s.marsh
[…]root@SAMBA:~# wbinfo -g
domain computers
domain controllers
schema admins
enterprise admins
domain users
domain guests
[…]- Use the
getenttool to verify that domain users and groups are correctly integrated into the local system database:
root@SAMBA:~# getent passwd
[…]
administrator:*:10500:10513::/home/administrator:/bin/bash
s.marsh:*:11115:10513::/home/s.marsh:/bin/bash
k.brofloski:*:11116:10513::/home/k.brofloski:/bin/bash
b.stotch:*:11117:10513::/home/b.stotch:/bin/bash
[…]root@SAMBA:~# getent group
[…]
domain admins:x:10512:
domain users:x:10513:
[…]- Set ownership of the shared directory to the appropriate domain user and group:
root@SAMBA:~# chown -R "administrator:domain users" /data/- Alternatively, use the corresponding UID and GID values:
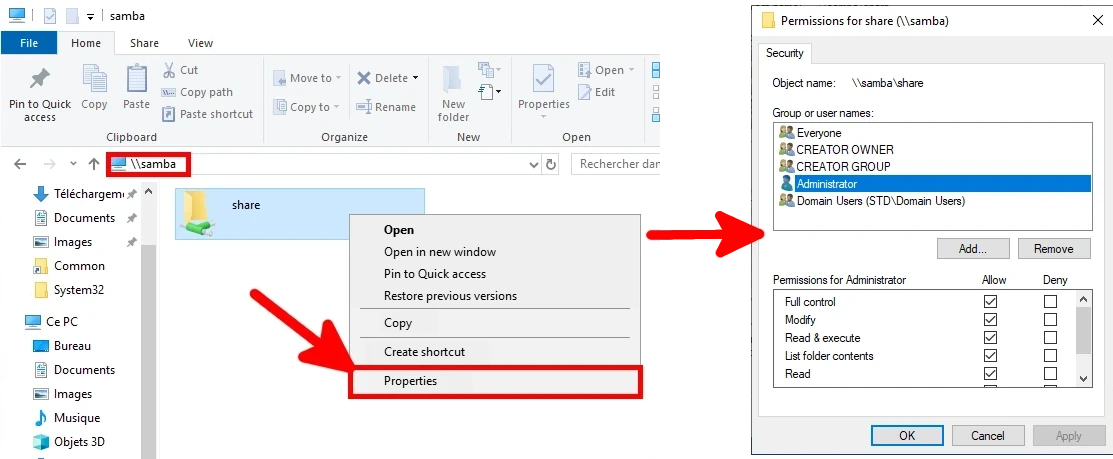
root@SAMBA:~# chown -R "10500:10513" /data/- Set permissions from the Active Directory server via the Windows GUI: