Enable and Run Signed PowerShell Scripts in Windows
- Last updated: Nov 24, 2024

By default, PowerShell scripts are restricted from running for security reasons. While the -ExecutionPolicy Bypass switch can override this restriction, it's not the most secure option. If you want to enhance security, it's worth exploring how to allow only signed scripts to run. Here, we'll look at how to create and authorize only signed scripts.
Group Policy to allow signed scripts only
- Open the Group Policy editor:
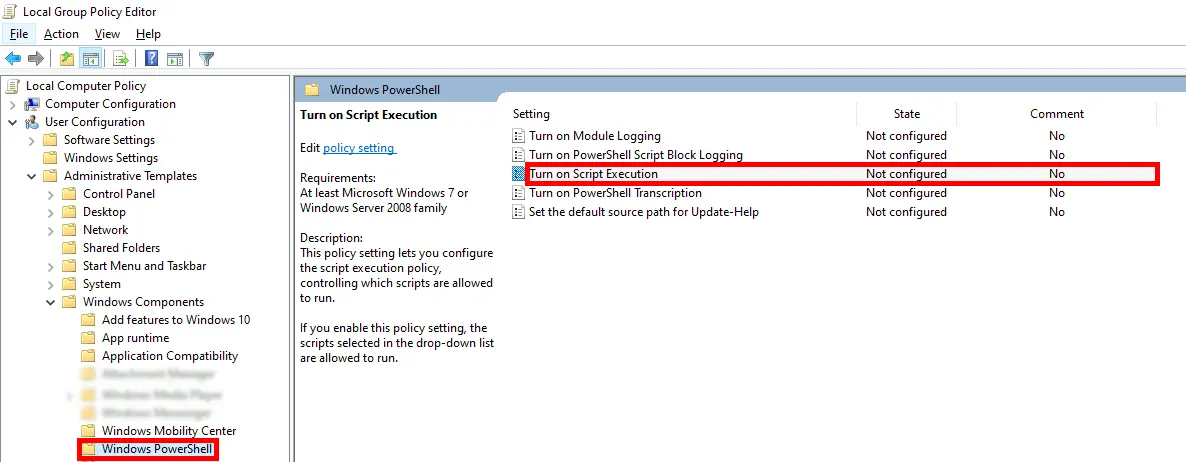
- Go to User Configuration > Administrative Templates > Windows Components > Windows PowerShell:
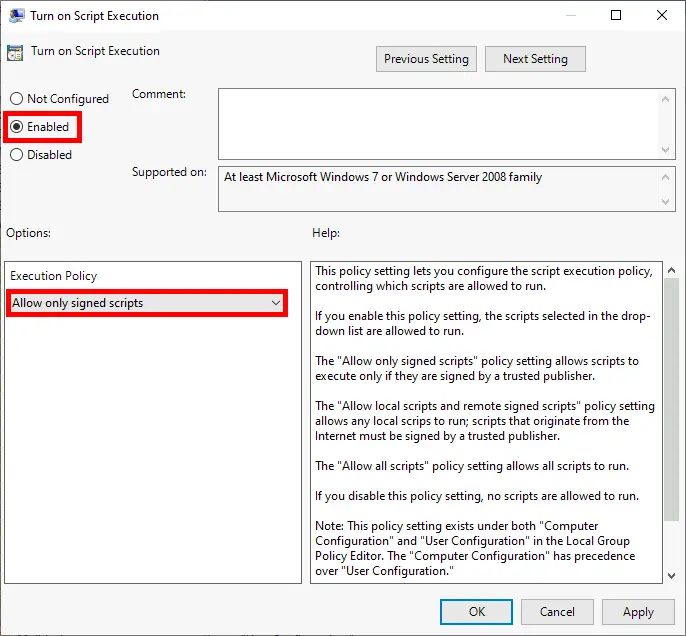
- Edit the Turn on Script Execution policy:
Create Certificate
To sign our scripts, we need a certificate. Here's how to create a self-signed certificate.
- Open Windows PowerShell as administrator:
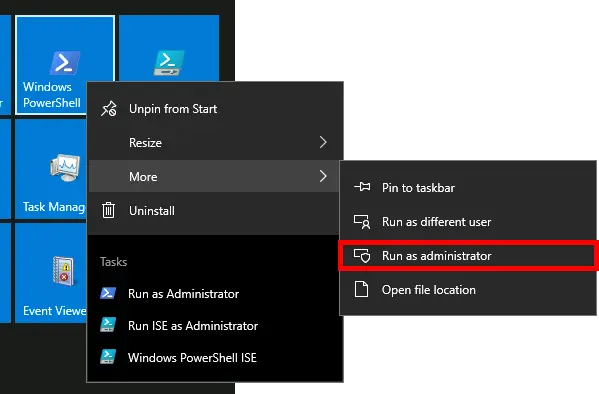
- Set a name for your new certificate in the variable
$CertificateName:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> $CertificateName = "STD Certificate"- Define where you want to create your certificate:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> $OutPutPFXFilePath = "C:\Users\administrator\Desktop\MyNewSigningCertificate.pfx"- Set password for the pfx container:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> $MyStrongPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString -String "MyPassword" -Force -AsPlainText- Finaly, create the certificate with a lifetime of 10 years and a key size of 4096 bits:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> New-SelfSignedCertificate -subject $CertificateName -Type CodeSigning -NotAfter (Get-Date).AddYears(10) -KeyLength 4096 | Export-PfxCertificate -FilePath $OutPutPFXFilePath -password $MyStrongPasswordSigning the script
- Load the certificate:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> $MyCertFromPfx = Get-PfxCertificate -FilePath 'C:\Users\administrator\Desktop\MyNewSigningCertificate.pfx'
Enter password : ********- Signing the script:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> Set-AuthenticodeSignature -PSPath 'C:\Users\administrator\Desktop\script.ps1' -Certificate $MyCertFromPfx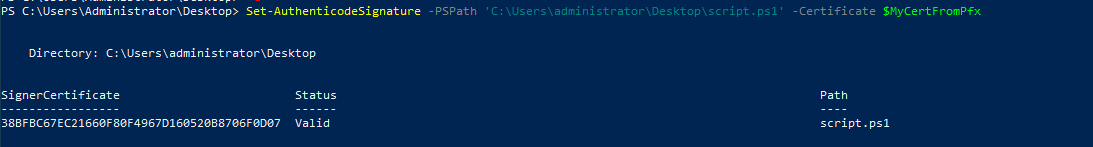
Importing the certificate
To be correctly recognized, a self-signed certificate must be imported on the computers on which we want to run the PowerShell scripts. Type the following commands with administrator rights.
Set variables
- Set the pfx password and certificate path:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> $MyStrongPassword = ConvertTo-SecureString -String "MyPassword" -Force -AsPlainTextPS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> $CertPath = "C:\Users\administrator\Desktop\MyNewSigningCertificate.pfx"Import to Trusted Root Certification Authorities store
- Import the certificate into the Trusted Root Certification Authorities local computer store:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> Import-PfxCertificate -FilePath $CertPath "cert:\LocalMachine\Root" -Password $MyStrongPassword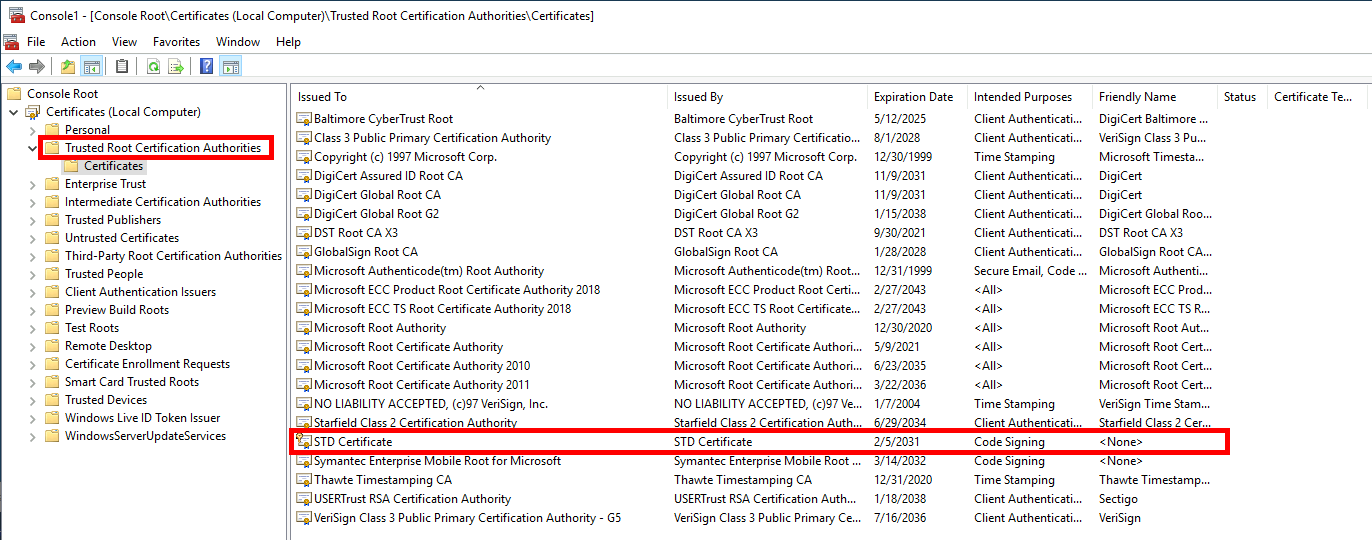
Import to Trusted Publishers store
- Import the certificate to the Trusted Publishers local computer store:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> Import-PfxCertificate -FilePath $CertPath "cert:\LocalMachine\TrustedPublisher" -Password $MyStrongPassword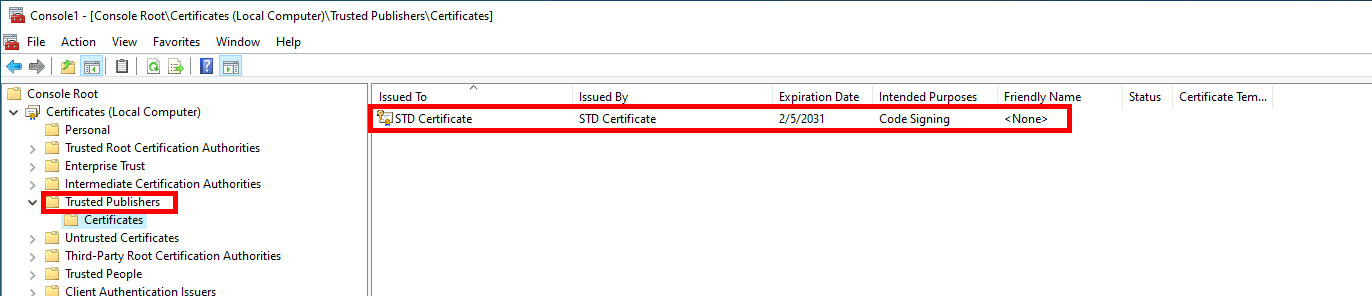
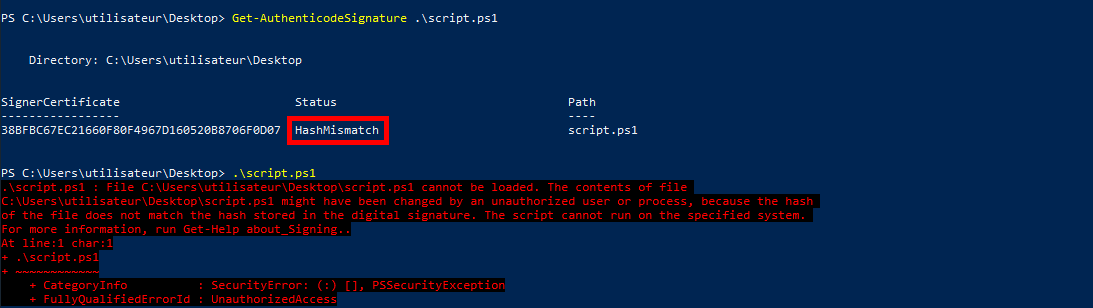
Check script signature
- We can check whether the script is correctly signed using the
Get-AuthenticodeSignaturecommand:
PS C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop> Get-AuthenticodeSignature 'C:\Users\administrator\Desktop\script.ps1'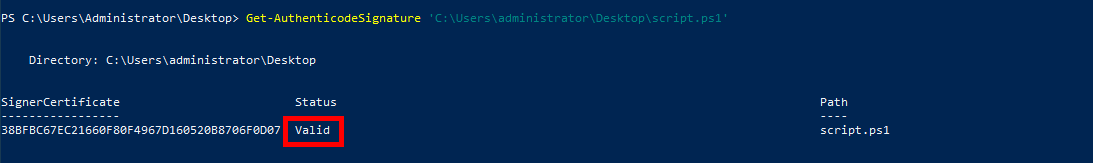
- If the script has been altered after being signed, the HashMismacth status appears and the script cannot be executed: