How to Enable File Auditing on a Windows File Server
- Last updated: Oct 14, 2025

As a system administrator, you’ve probably dealt with users complaining about files mysteriously disappearing or being modified without explanation.
To identify who accessed, changed, or deleted data on your Windows File Server, you can enable file auditing. This feature records every file access event and helps ensure data security and accountability across your network.
In this guide, we’ll show you step by step how to configure Windows file auditing using Group Policy and view detailed logs in Event Viewer.
Configure File Auditing via Group Policy (GPO)
To enable file auditing we need to create a new GPO.
Create a GPO for File Auditing
- Open the Group Policy Management Console on your Windows Server to begin creating the file auditing policy.
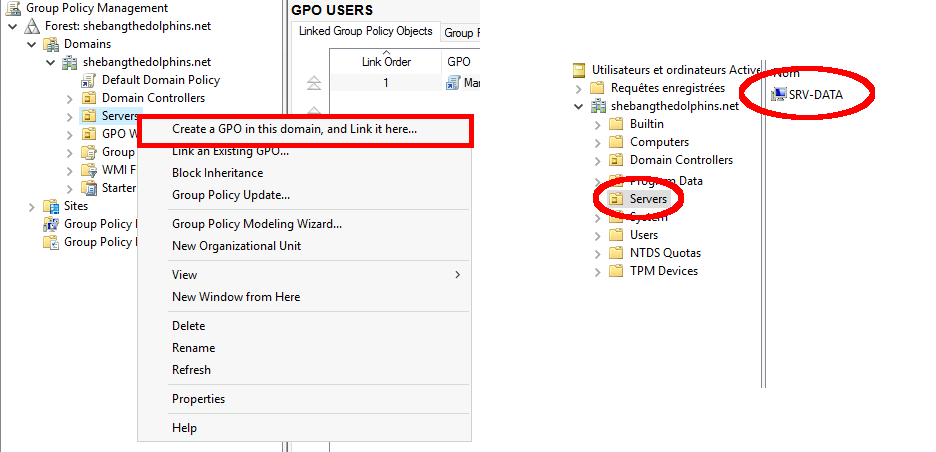
- Create a new Group Policy Object (GPO) and link it to the Organizational Unit (OU) that contains your Windows file server. This ensures the file auditing policy will apply correctly to the target server.
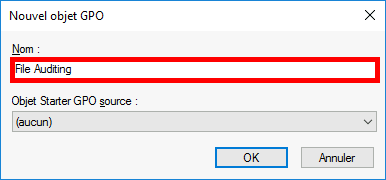
- Give the GPO a name, for example File Auditing:
Configure the GPO for Windows File Auditing
- Edit the newly created Group Policy Object (GPO) to configure the Windows file auditing policy.
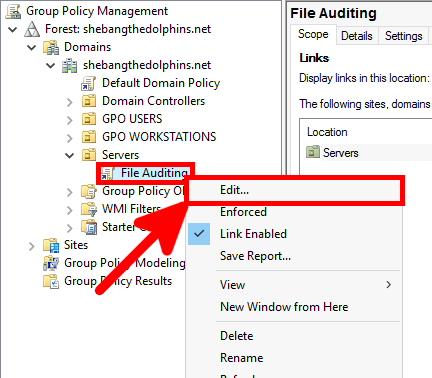
- In the Group Policy Management Editor, navigate to Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Local Policies > Audit Policy:
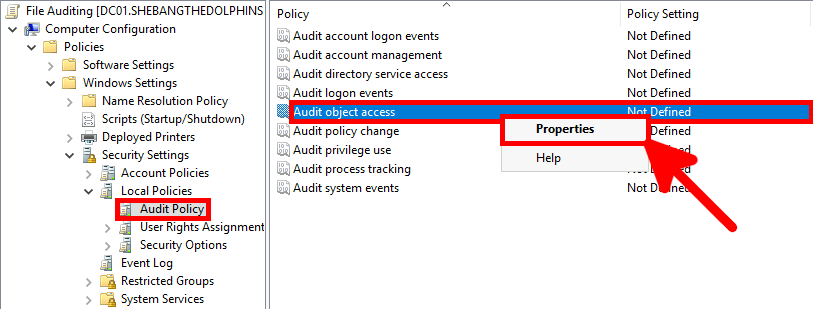
- Select both Success and Failure to log all file access attempts, then click OK to apply the Windows file auditing policy.
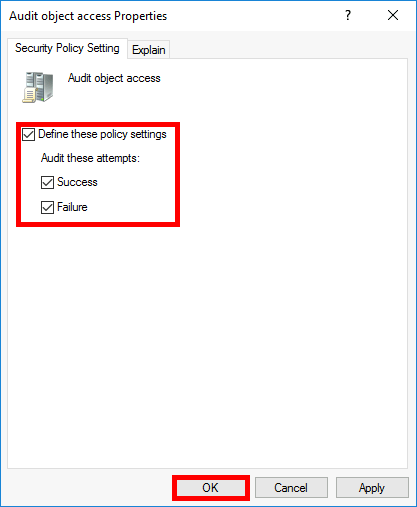
- Go to Computer Configuration > Policies > Windows Settings > Security Settings > Advanced Audit Policy Configuration > Audit Policies > Object Access, then edit Audit File System:
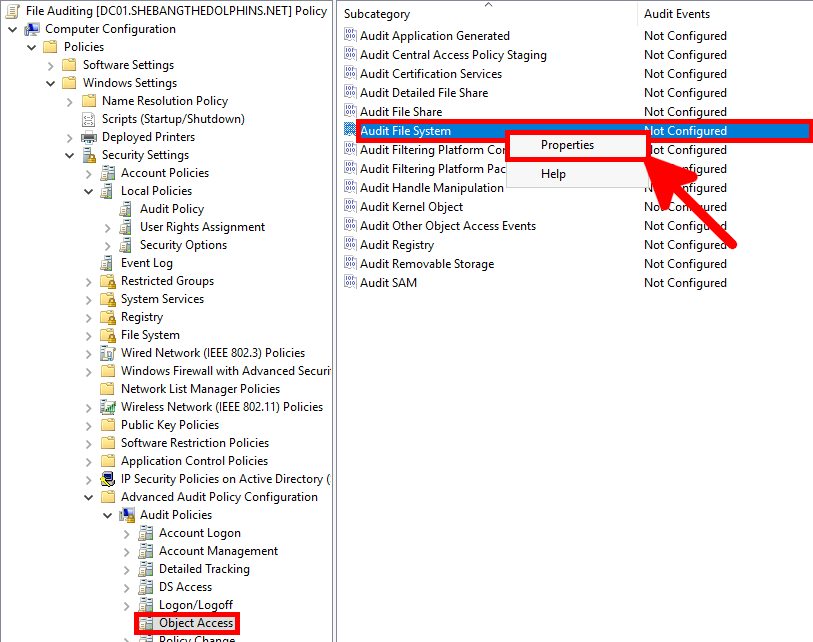
- Select both Success and Failure to record all file access attempts, then click OK to apply the Windows file auditing settings.
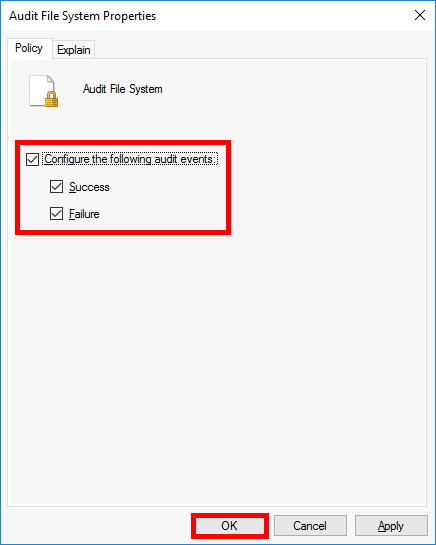
Configure File Auditing on the Windows File Server
We now need to connect to our Windows File Server to enable File Auditing on a folder.
Enable File Auditing on the Windows File Server
In this example, we’ll enable Windows file auditing on the shared folder \\SRV-DATA\01-Admin to track file access and modification events.
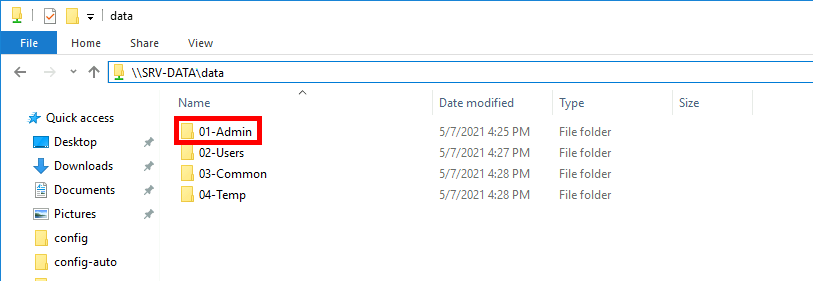
- Right-click the folder on your Windows File Server and select Properties to configure file auditing.
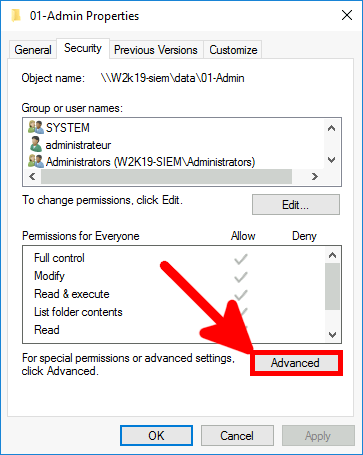
- Go to the Security tab of the folder properties and click Advanced to configure Windows file auditing.
- In the Advanced Security Settings window, go to the Auditing tab and click Add to create a new Windows file auditing entry.
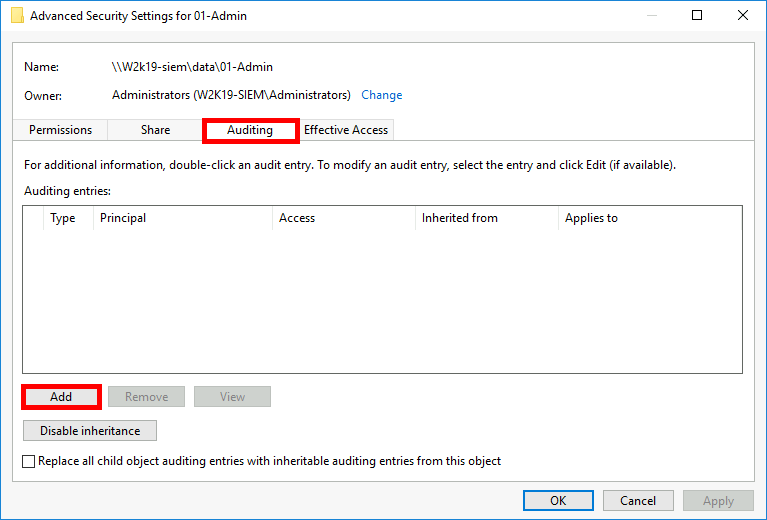
- Click the Select a principal link to choose the user or group you want to audit.
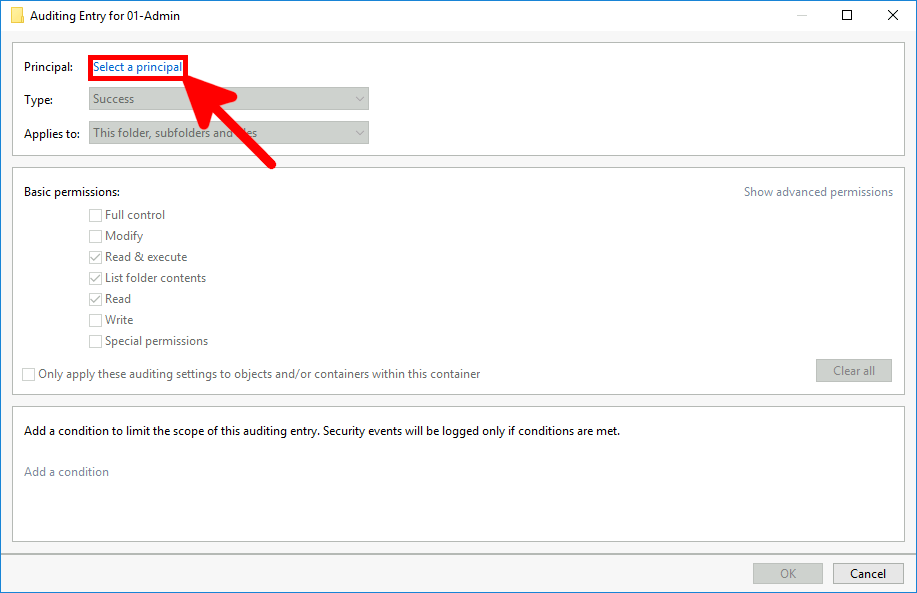
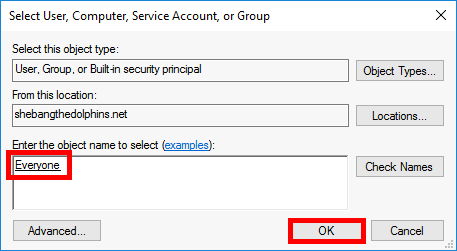
- Add the Everyone group as the principal to audit all user access on the folder.
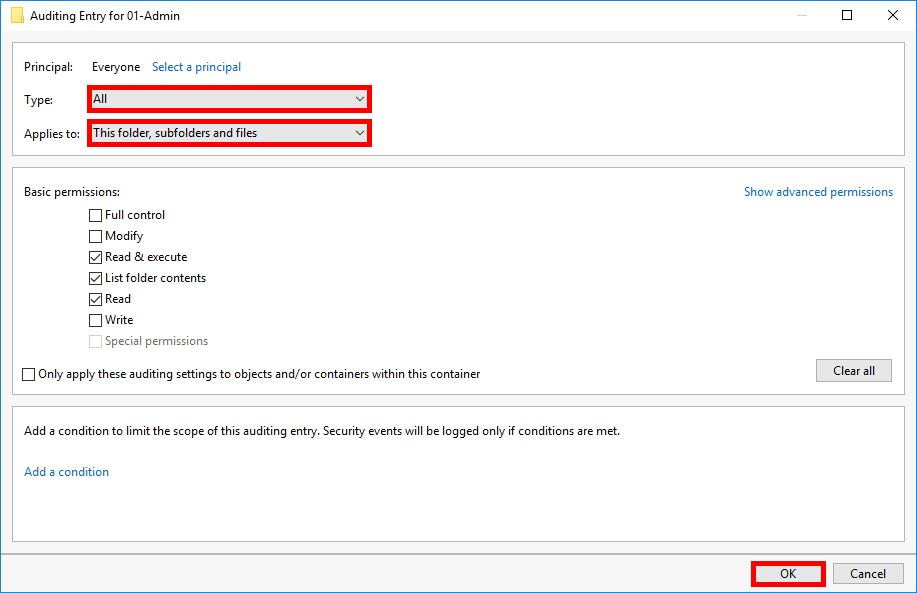
- Select All permissions and choose This folder, subfolders and files, then click OK to apply the Windows file auditing rule.
Check if the File Auditing GPO is Applied
- You can verify that the Group Policy Object (GPO) for Windows file auditing is correctly applied using the
gpresultcommand:
C:\> gpresult /r /z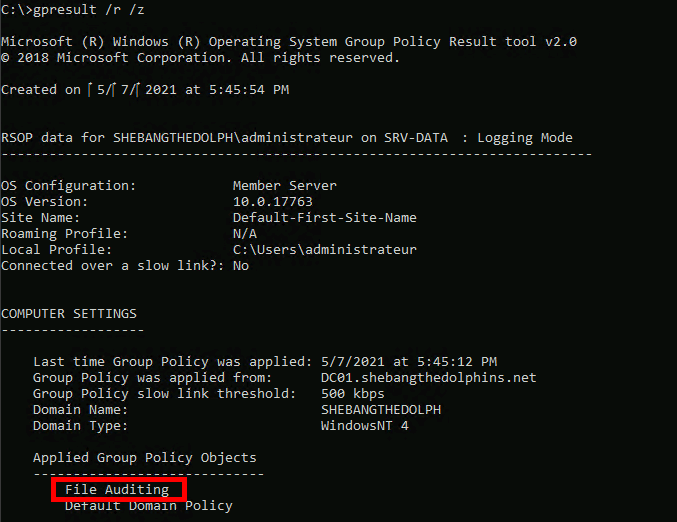
View Windows File Auditing Logs
The Windows file auditing events are recorded in the Security log of the Event Viewer.
- Open the Event Viewer and navigate to Windows Logs > Security:
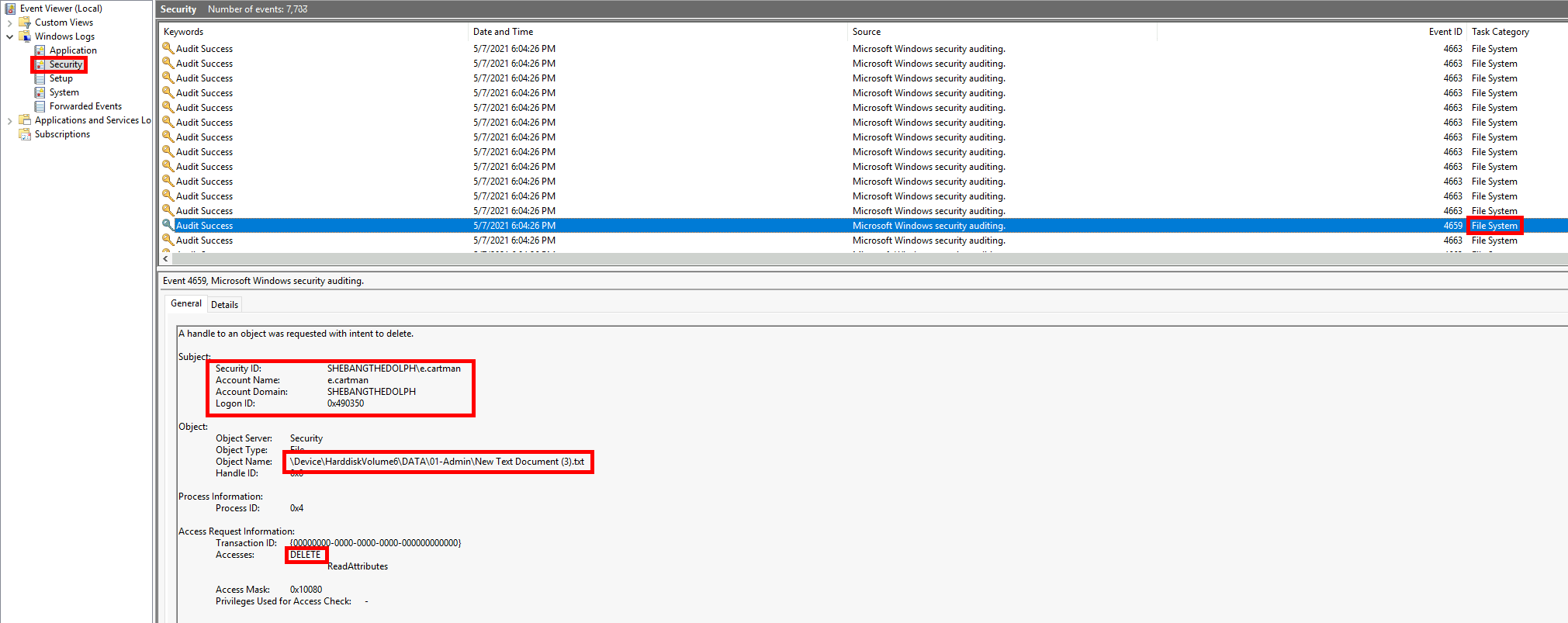
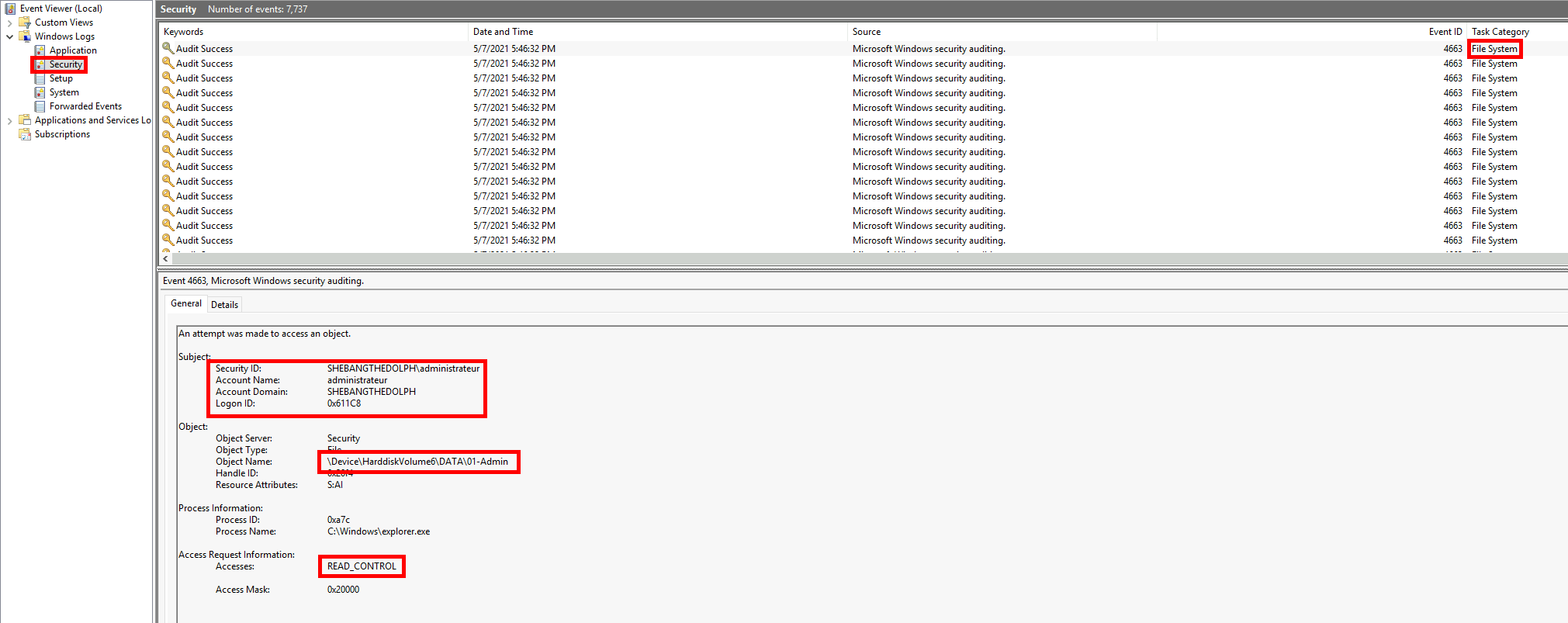
- Here is an example from the Windows file auditing log showing a Read access to the «01-Admin» folder by the administrateur account:
- This example from the Windows file auditing log shows the file «New Text Document (3)» being deleted by the e.cartman account: