Configurer la QoS sur GNU/Linux avec la commande tc
- Mise à jour le 12 avril 2025

Intro
Sur un système GNU/Linux, la QoS peut être mise en place avec la commande tc. D'après wikipedia tc (traffic control) est l'outil utilisé pour configurer l'ordonnanceur de paquets du noyau Linux. Dans cet article, quelques commandes et un exemple concret pour voir comment l'utiliser.
Comme nous le verrons la gestion du trafic dans GNU/Linux n'est pas très simple…
Commandes principales
Limiter le téléchargement (ingress) rate
Comme on peut le voir sur l'image ci-dessous, le trafic sortant/egress passe directement par l'interface eth0 vers internet, alors que le trafic entrant/ingress traversera eth0 puis l'interface ifb0 en vue d'être régulé puis redirigé vers eth0.
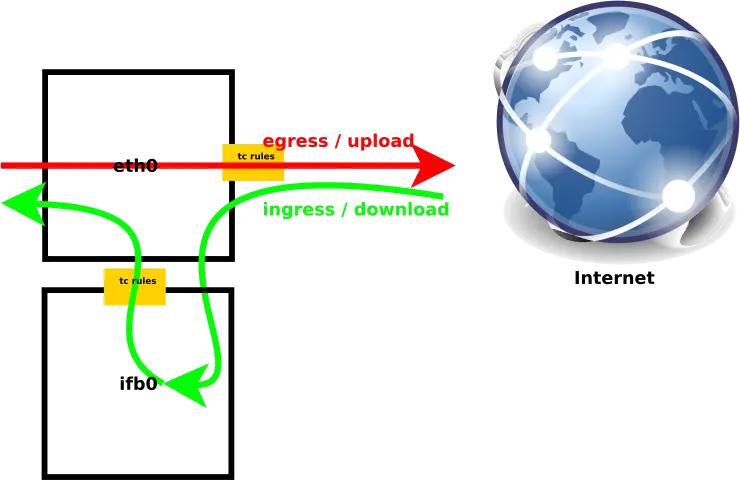
Pour créer notre interface ifb nous aurons besoin de charger le module et activer l'interface.
- Charger le module
ifbpour une interface (numifbs=1) :
root@host:~# modprobe ifb numifbs=1- Activer l'interface
ifb0:
root@host:~# ip link set dev ifb0 up- Créer une règle pour le trafic entrant :
root@host:~# tc qdisc add dev eth0 ingress handle ffff:- Transférer le trafic entrant de
eth0vers l'interfaceifb0:
root@host:~# tc filter add dev eth0 parent ffff: protocol all u32 match u32 0 0 action mirred egress redirect dev ifb0- Par exemple, créons une règle pour le trafic entrant afin de limiter tous les téléchargement à 1Mb/s sur l'interface
eth0 (ifb0):
root@host:~# tc qdisc add dev ifb0 root handle 2: htb default 1root@host:~# tc class add dev ifb0 parent 2: classid 2:1 htb rate 1024kbitVoir l'application des règles en temps réel
- Installer l'outile
watch:
root@host:~# apt install watch- Pour le trafic entrant (téléchargement) :
root@host:~# watch -n 1 tc -s class show dev ifb0- Pour le trafic sortant (upload) :
root@host:~# watch -n 1 tc -s class show dev eth0Réinitialiser les règles
Si l'on souhaite réinitialiser/désactiver la QoS nous devrons entrer les commandes suivantes.
- Pour l'ingress (téléchargement), c'est au niveau de l'interface
ifb0:
root@host:~# ip link set dev ifb0 downroot@host:~# tc qdisc del dev eth0 rootroot@host:~# tc qdisc del dev ifb0 root- Pour l'egress (upload), c'est au niveau de l'interface
eth0:
root@host:~# tc qdisc del dev eth0 ingressroot@host:~# tc qdisc del dev ifb0 ingressExemple pratique pour faire de la QoS sur un routeur NAT
Imaginons que l'on dispose d'une connexion internet à 1Gb/s symétrique et que l'on souhaite répartir la bande passante sur les trois réseaux suivants : Servers, Users et WiFi. Pour être efficace la QoS ne sera appliqué que sur 90% de la bande passante maximale (donc 900Mb/s dans notre cas).
Répartition de la bande passante
- Voici comment on souhaite organiser notre trafic :
- Servers :
- Téléchargement : max 900Mb/s, min 400Mb/s
- Upload : max 900Mb/s, min 700Mb/s
- Users :
- Téléchargement : max 500Mb/s, min 200Mb/s
- Upload : max 200Mb/s, min 100Mb/s
- WiFi :
- Téléchargement : max 200Mb/s, min 100Mb/s
- Upload : max 100Mb/s, min 80Mb/s
- Servers :
Architecture
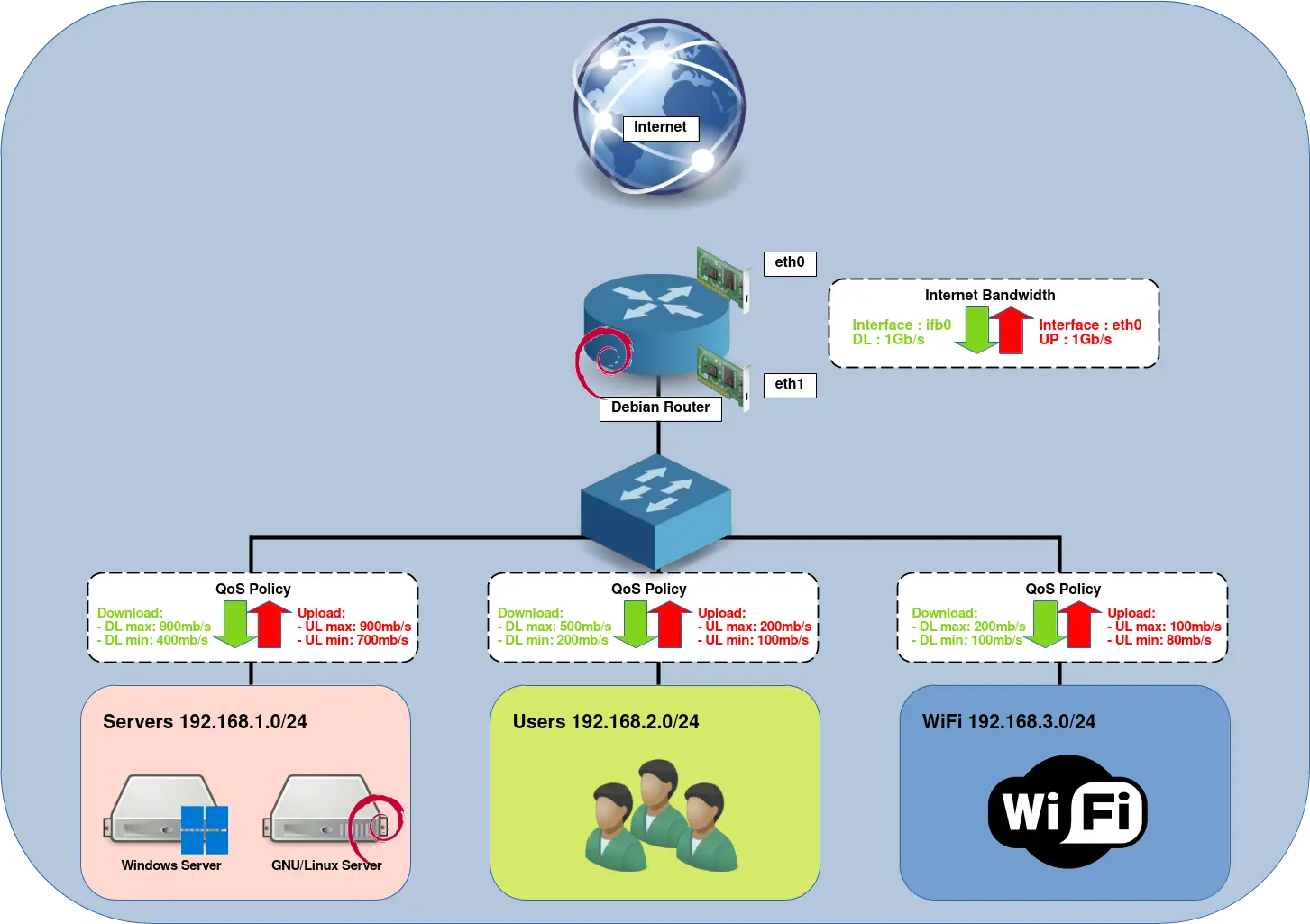
Script
- Le script complet pour l'application de la QoS :
#!/bin/sh
# load modules
modprobe ifb numifbs=1
modprobe sch_fq_codel
modprobe act_mirred
#modprobe br_netfilter #in order to netfilter aware about bridge traffic
modprobe act_connmark #https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/155751/setting-traffic-class-on-return-packets
#QoS reset
for IFB in ifb0 ; do
ip link set dev $IFB down
done
for IF in eth0 ifb0 ; do
tc qdisc del dev $IF root 2> /dev/null > /dev/null
tc qdisc del dev $IF ingress 2> /dev/null > /dev/null
done
for IFB in ifb0 ; do
ip link set dev $IFB up
done
#if we want to disable qos run the script with stop argument
if [ "$1" = "stop" ]; then
echo "stop"
iptables -F -t mangle
iptables -X -t mangle
exit 0
fi
###############################
#UPLOAD (egress traffic) RULES#
###############################
#RULES
tc qdisc add dev eth0 root handle 1: htb default 10
tc class add dev eth0 parent 1: classid 1:1 htb rate 900mbit #here we set our max Bandwidth
##Servers (192.168.1.0 network) and default (if no matching case)
tc class add dev eth0 parent 1:1 classid 1:10 htb rate 700mbit ceil 900mbit prio 1
##Users (192.168.2.0 network)
tc class add dev eth0 parent 1:1 classid 1:20 htb rate 100mbit ceil 200mbit prio 2
##WiFi (192.168.3.0 network)
tc class add dev eth0 parent 1:1 classid 1:30 htb rate 100mbit ceil 80mbit prio 3
#FILTERS
##Servers (192.168.1.0 network); handle 1 means mark 1 (see iptables rules)
tc filter add dev eth0 parent 1:0 protocol ip prio 1 handle 1 fw classid 1:10
##Users (192.168.2.0 network); handle 2 means mark 2 (see iptables rules)
tc filter add dev eth0 parent 1:0 protocol ip prio 2 handle 2 fw classid 1:20
##WiFi (192.168.3.0 network); handle 3 means mark 3 (see iptables rules)
tc filter add dev eth0 parent 1:0 protocol ip prio 3 handle 3 fw classid 1:30
## Martin Devera, author of HTB, then recommends SFQ for beneath these classes :
tc qdisc add dev eth0 parent 1:10 handle 110: sfq perturb 10
tc qdisc add dev eth0 parent 1:20 handle 120: sfq perturb 10
tc qdisc add dev eth0 parent 1:30 handle 130: sfq perturb 10
##################################
#DOWNLOAD (ingress traffic) RULES#
##################################
#RULES
tc qdisc add dev ifb0 root handle 2: htb default 10
tc class add dev ifb0 parent 2: classid 2:1 htb rate 900mbit #here we set our max Bandwidth
##Servers (192.168.1.0 network) and default (if no matching case)
tc class add dev ifb0 parent 2:1 classid 2:10 htb rate 400mbit ceil 900mbit prio 1
##Users (192.168.2.0 network)
tc class add dev ifb0 parent 2:1 classid 2:20 htb rate 200mbit ceil 500mbit prio 2
##WiFi (192.168.3.0 network)
tc class add dev ifb0 parent 2:1 classid 2:30 htb rate 100mbit ceil 200mbit prio 3
#FILTERS
##Servers (192.168.1.0 network); handle 1 means mark 1 (see iptables rules)
tc filter add dev ifb0 parent 2:0 protocol ip prio 1 handle 1 fw flowid 2:10
##Users (192.168.2.0 network); handle 2 means mark 2 (see iptables rules)
tc filter add dev ifb0 parent 2:0 protocol ip prio 2 handle 2 fw flowid 2:20
##WiFi (192.168.3.0 network); handle 3 means mark 3 (see iptables rules)
tc filter add dev ifb0 parent 2:0 protocol ip prio 3 handle 4 fw flowid 2:30
#Create ingress on external interface
tc qdisc add dev eth0 ingress handle ffff:
#Forward all ingress traffic to the IFB device
#tc filter add dev eth0 parent ffff: protocol all u32 match u32 0 0 action mirred egress redirect dev ifb0
tc filter add dev eth0 parent ffff: protocol ip u32 match u32 0 0 action connmark action mirred egress redirect dev ifb0 flowid ffff:1
##########
#IPTABLES#
##########
#Flush mangle rules
iptables -F -t mangle
iptables -X -t mangle
iptables -t mangle -N QOS
iptables -t mangle -A FORWARD -o eth0 -j QOS
iptables -t mangle -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -j QOS
iptables -t mangle -A QOS -j CONNMARK --restore-mark
iptables -t mangle -A QOS -m mark ! --mark 0 -j ACCEPT
iptables -t mangle -A QOS -s 192.168.1.0/24 -m mark --mark 0 -j MARK --set-mark 1
iptables -t mangle -A QOS -s 192.168.2.0/24 -m mark --mark 0 -j MARK --set-mark 2
iptables -t mangle -A QOS -s 192.168.3.0/24 -m mark --mark 0 -j MARK --set-mark 3
iptables -t mangle -A QOS -p icmp -j MARK --set-mark 0x1
iptables -t mangle -A QOS -p tcp -m tcp --sport 22 -j MARK --set-mark 0x1
#iptables -t mangle -I QOS -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST,ACK SYN -j MARK --set-mark 0x1
iptables -t mangle -A QOS -j CONNMARK --save-mark
#(optionnal) set mark to give priority to ssh, icmp and packets initiating a tcp connection (SYN flags activated). see : https://inetdoc.net/guides/lartc/lartc.cookbook.fullnat.intro.html
iptables -t mangle -A PREROUTING -p icmp -j MARK --set-mark 0x1
iptables -t mangle -A PREROUTING -p tcp -m tcp --sport 22 -j MARK --set-mark 0x1
iptables -t mangle -I PREROUTING -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST,ACK SYN -j MARK --set-mark 0x1- On pourra vérifier que les paquets sont corectements marquées avec l'outil
conntrack:
root@host:~# apt-get install conntrackroot@host:~# conntrack -L | grep 'mark=1'- Pour les
iptables-phobique (ou lesnftablesenthousiastes), on pourra marquer le trafic avec ce fichiernftables.conf:
flush ruleset
table ip mangle {
chain QOS_UPLOAD {
type filter hook output priority -150;
ip saddr { 192.168.1.0/24 } counter meta mark set 1
ip saddr { 192.168.2.0/24 } counter meta mark set 2
ip saddr { 192.168.3.0/24 } counter meta mark set 3
}
chain QOS_DOWNLOAD {
type filter hook forward priority -150;
ip daddr { 192.168.1.0/24 } counter meta mark set 1
ip daddr { 192.168.1.0/24 } counter ct mark set mark
ip daddr { 192.168.2.0/24 } counter meta mark set 2
ip daddr { 192.168.2.0/24 } counter ct mark set mark
ip daddr { 192.168.3.0/24 } counter meta mark set 3
ip daddr { 192.168.3.0/24 } counter ct mark set mark
#ip daddr 192.168.3.0/24 counter meta mark set ct mark
}
}