Configure QoS on GNU/Linux with the tc Command
- Last updated: Apr 12, 2025

Intro
On GNU/Linux systems, quality of service can be set and managed using the tc command. According to wikipedia (source: https://en.wikipedia.org/), tc (for traffic control) is the user-space utility program used to configure the Linux kernel packet scheduler. In this article, we'll look at a few examples to show how we can use it.
As we will see, GNU/Linux traffic control isn't that simple… Let's see here how it works.
Main Commands
Limit download (ingress) rate
As you can see on the image below, the upload/egress traffic goes directly from eth0 to the internet, while the download/ingress traffic goes to eth0 through the ifb0 interface to be traffic shaped before returning to eth0.
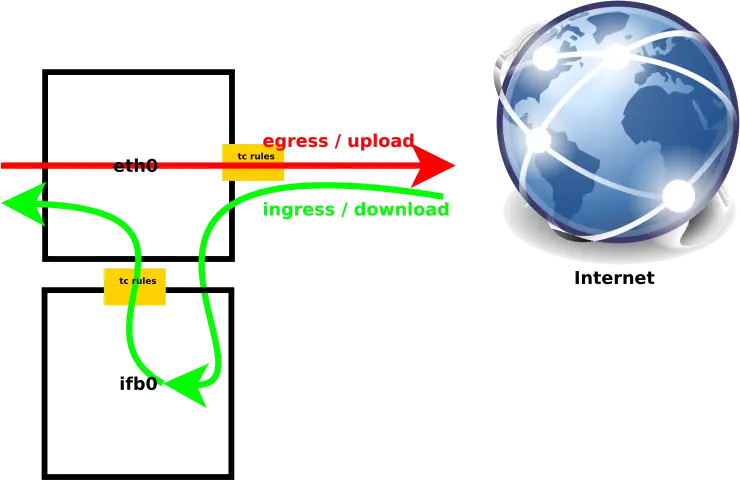
In order to create our ifb interface we need to load the module and bring the interface up.
- Load
ifbmodule for one interface (numifbs=1):
root@host:~# modprobe ifb numifbs=1- Enable
ifb0interface:
root@host:~# ip link set dev ifb0 up- Create ingress:
root@host:~# tc qdisc add dev eth0 ingress handle ffff:- Forward all ingress traffic from
eth0to theifb0interface:
root@host:~# tc filter add dev eth0 parent ffff: protocol all u32 match u32 0 0 action mirred egress redirect dev ifb0- And, for example, create ingress rules to limit all download traffic at 1Mb/s on
eth0 (ifb0)interface:
root@host:~# tc qdisc add dev ifb0 root handle 2: htb default 1root@host:~# tc class add dev ifb0 parent 2: classid 2:1 htb rate 1024kbitShow real time rules
- Install
watchcommand:
root@host:~# apt install watch- For ingress (download) traffic:
root@host:~# watch -n 1 tc -s class show dev ifb0- For egress (upload) traffic:
root@host:~# watch -n 1 tc -s class show dev eth0Reinit rules
If we want to reset/disable our QoS rules we have to type the following commands.
- For ingress, ifb0 interface:
root@host:~# ip link set dev ifb0 downroot@host:~# tc qdisc del dev eth0 rootroot@host:~# tc qdisc del dev ifb0 root- For egress,
eth0interface:
root@host:~# tc qdisc del dev eth0 ingressroot@host:~# tc qdisc del dev ifb0 ingressPractical example of QoS on a NAT router
Let's say we have a 1Gb/s Internet connection and we want to share Bandwidth on these three networks : Servers, Users and WiFi. To be efficient the QoS needs to be applied on approximatively 90% of total Bandwidth (900Mb/s in this case).
Bandwidth allocation
- Here's how we want to share it:
- Servers:
- Download: max 900Mb/s, min 400Mb/s
- Upload: max 900Mb/s, min 700Mb/s
- Users:
- Download: max 500Mb/s, min 200Mb/s
- Upload: max 200Mb/s, min 100Mb/s
- WiFi:
- Download: max 200Mb/s, min 100Mb/s
- Upload: max 100Mb/s, min 80Mb/s
- Servers:
Architecture
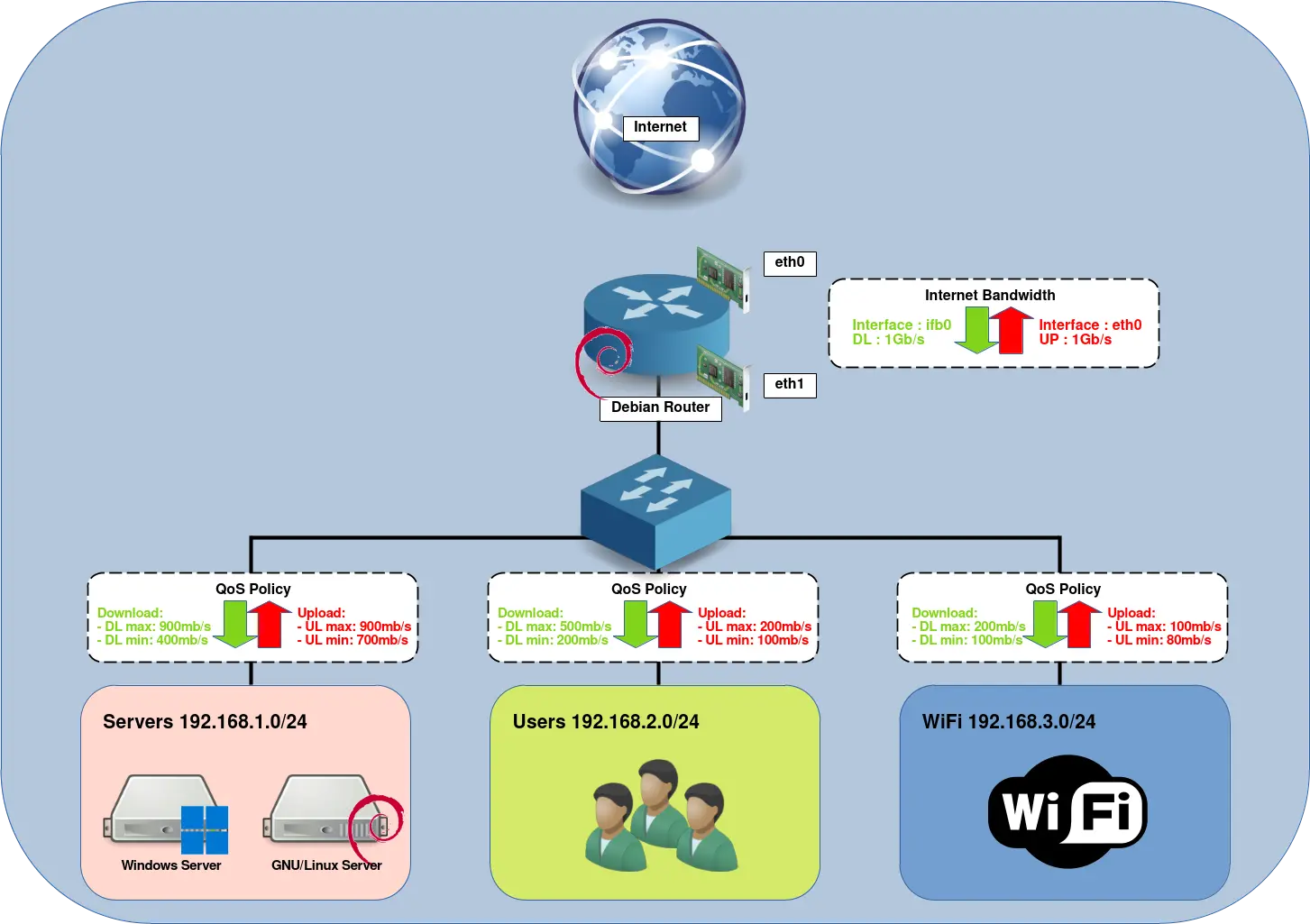
Script
- Full script to apply QoS rules:
#!/bin/sh
# load modules
modprobe ifb numifbs=1
modprobe sch_fq_codel
modprobe act_mirred
#modprobe br_netfilter #in order to netfilter aware about bridge traffic
modprobe act_connmark #https://unix.stackexchange.com/questions/155751/setting-traffic-class-on-return-packets
#QoS reset
for IFB in ifb0 ; do
ip link set dev $IFB down
done
for IF in eth0 ifb0 ; do
tc qdisc del dev $IF root 2> /dev/null > /dev/null
tc qdisc del dev $IF ingress 2> /dev/null > /dev/null
done
for IFB in ifb0 ; do
ip link set dev $IFB up
done
#if we want to disable qos run the script with stop argument
if [ "$1" = "stop" ]; then
echo "stop"
iptables -F -t mangle
iptables -X -t mangle
exit 0
fi
###############################
#UPLOAD (egress traffic) RULES#
###############################
#RULES
tc qdisc add dev eth0 root handle 1: htb default 10
tc class add dev eth0 parent 1: classid 1:1 htb rate 900mbit #here we set our max Bandwidth
##Servers (192.168.1.0 network) and default (if no matching case)
tc class add dev eth0 parent 1:1 classid 1:10 htb rate 700mbit ceil 900mbit prio 1
##Users (192.168.2.0 network)
tc class add dev eth0 parent 1:1 classid 1:20 htb rate 100mbit ceil 200mbit prio 2
##WiFi (192.168.3.0 network)
tc class add dev eth0 parent 1:1 classid 1:30 htb rate 100mbit ceil 80mbit prio 3
#FILTERS
##Servers (192.168.1.0 network); handle 1 means mark 1 (see iptables rules)
tc filter add dev eth0 parent 1:0 protocol ip prio 1 handle 1 fw classid 1:10
##Users (192.168.2.0 network); handle 2 means mark 2 (see iptables rules)
tc filter add dev eth0 parent 1:0 protocol ip prio 2 handle 2 fw classid 1:20
##WiFi (192.168.3.0 network); handle 3 means mark 3 (see iptables rules)
tc filter add dev eth0 parent 1:0 protocol ip prio 3 handle 3 fw classid 1:30
## Martin Devera, author of HTB, then recommends SFQ for beneath these classes :
tc qdisc add dev eth0 parent 1:10 handle 110: sfq perturb 10
tc qdisc add dev eth0 parent 1:20 handle 120: sfq perturb 10
tc qdisc add dev eth0 parent 1:30 handle 130: sfq perturb 10
##################################
#DOWNLOAD (ingress traffic) RULES#
##################################
#RULES
tc qdisc add dev ifb0 root handle 2: htb default 10
tc class add dev ifb0 parent 2: classid 2:1 htb rate 900mbit #here we set our max Bandwidth
##Servers (192.168.1.0 network) and default (if no matching case)
tc class add dev ifb0 parent 2:1 classid 2:10 htb rate 400mbit ceil 900mbit prio 1
##Users (192.168.2.0 network)
tc class add dev ifb0 parent 2:1 classid 2:20 htb rate 200mbit ceil 500mbit prio 2
##WiFi (192.168.3.0 network)
tc class add dev ifb0 parent 2:1 classid 2:30 htb rate 100mbit ceil 200mbit prio 3
#FILTERS
##Servers (192.168.1.0 network); handle 1 means mark 1 (see iptables rules)
tc filter add dev ifb0 parent 2:0 protocol ip prio 1 handle 1 fw flowid 2:10
##Users (192.168.2.0 network); handle 2 means mark 2 (see iptables rules)
tc filter add dev ifb0 parent 2:0 protocol ip prio 2 handle 2 fw flowid 2:20
##WiFi (192.168.3.0 network); handle 3 means mark 3 (see iptables rules)
tc filter add dev ifb0 parent 2:0 protocol ip prio 3 handle 4 fw flowid 2:30
#Create ingress on external interface
tc qdisc add dev eth0 ingress handle ffff:
#Forward all ingress traffic to the IFB device
#tc filter add dev eth0 parent ffff: protocol all u32 match u32 0 0 action mirred egress redirect dev ifb0
tc filter add dev eth0 parent ffff: protocol ip u32 match u32 0 0 action connmark action mirred egress redirect dev ifb0 flowid ffff:1
##########
#IPTABLES#
##########
#Flush mangle rules
iptables -F -t mangle
iptables -X -t mangle
iptables -t mangle -N QOS
iptables -t mangle -A FORWARD -o eth0 -j QOS
iptables -t mangle -A OUTPUT -o eth0 -j QOS
iptables -t mangle -A QOS -j CONNMARK --restore-mark
iptables -t mangle -A QOS -m mark ! --mark 0 -j ACCEPT
iptables -t mangle -A QOS -s 192.168.1.0/24 -m mark --mark 0 -j MARK --set-mark 1
iptables -t mangle -A QOS -s 192.168.2.0/24 -m mark --mark 0 -j MARK --set-mark 2
iptables -t mangle -A QOS -s 192.168.3.0/24 -m mark --mark 0 -j MARK --set-mark 3
iptables -t mangle -A QOS -p icmp -j MARK --set-mark 0x1
iptables -t mangle -A QOS -p tcp -m tcp --sport 22 -j MARK --set-mark 0x1
#iptables -t mangle -I QOS -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST,ACK SYN -j MARK --set-mark 0x1
iptables -t mangle -A QOS -j CONNMARK --save-mark
#(optional) set mark to give priority to ssh, icmp and packets initiating a tcp connection (SYN flags activated). see : https://inetdoc.net/guides/lartc/lartc.cookbook.fullnat.intro.html
iptables -t mangle -A PREROUTING -p icmp -j MARK --set-mark 0x1
iptables -t mangle -A PREROUTING -p tcp -m tcp --sport 22 -j MARK --set-mark 0x1
iptables -t mangle -I PREROUTING -p tcp -m tcp --tcp-flags SYN,RST,ACK SYN -j MARK --set-mark 0x1- We can check that our frames are correctly marked with the conntrack tool:
root@host:~# apt-get install conntrackroot@host:~# conntrack -L | grep 'mark=1'- If we don't like
iptableswe canmarktraffic with thisnftables.conffile:
flush ruleset
table ip mangle {
chain QOS_UPLOAD {
type filter hook output priority -150;
ip saddr { 192.168.1.0/24 } counter meta mark set 1
ip saddr { 192.168.2.0/24 } counter meta mark set 2
ip saddr { 192.168.3.0/24 } counter meta mark set 3
}
chain QOS_DOWNLOAD {
type filter hook forward priority -150;
ip daddr { 192.168.1.0/24 } counter meta mark set 1
ip daddr { 192.168.1.0/24 } counter ct mark set mark
ip daddr { 192.168.2.0/24 } counter meta mark set 2
ip daddr { 192.168.2.0/24 } counter ct mark set mark
ip daddr { 192.168.3.0/24 } counter meta mark set 3
ip daddr { 192.168.3.0/24 } counter ct mark set mark
#ip daddr 192.168.3.0/24 counter meta mark set ct mark
}
}