Configuring Secure NFS with Kerberos Authentication and Encryption
- Last updated: Jun 21, 2025
I needed to set up a shared directory on my network. Since I'm working in a GNU/Linux environment, NFS was the natural choice.
However, NFS lacks built-in security by default. It relies solely on IP filtering, which is weak, offering no authentication or encryption.
To address these limitations, one option is to use a VPN; another is to rely on the Kerberos protocol. As I had never used Kerberos before, I chose to explore it.
- This guide walks through setting up an NFS + Kerberos architecture with the following setup:
- Debian Server: acts as both the NFS server and the Kerberos Key Distribution Center (KDC)
- ArchLinux Client: NFS client
- Debian Client: NFS client
Network Architecture
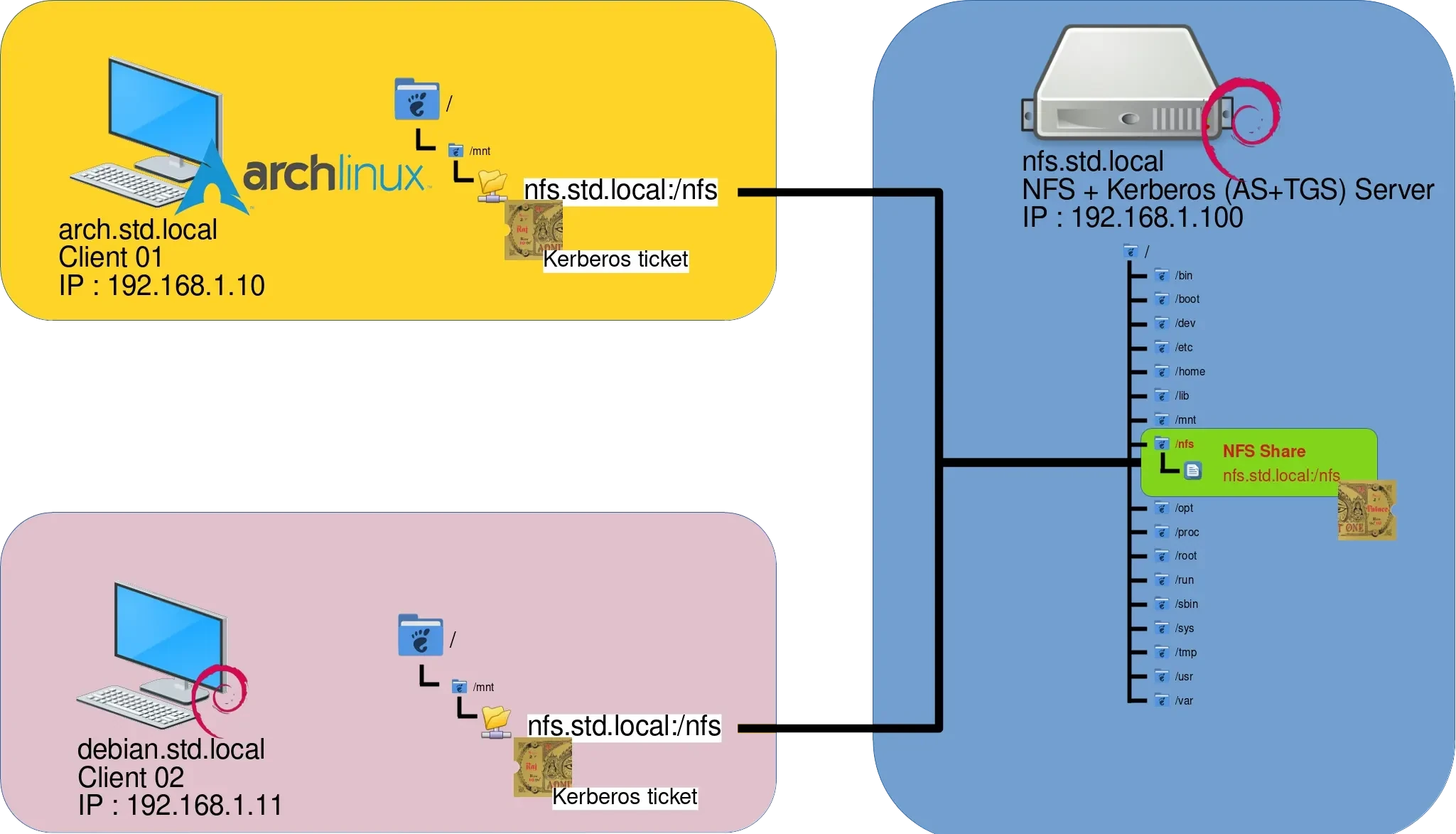
Server
Install
- Edit
/etc/network/interfacesto assign a static IP address:
allow-hotplug ens192
iface ens192 inet static
address 192.168.1.100
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 192.168.1.254
dns-nameservers 192.168.1.254- Install the required packages:
root@debian:~# apt update && apt install nfs-kernel-server nfs-common krb5-user libpam-krb5 krb5-admin-server krb5-kdc- Create the nfs group:
root@debian:~# groupadd nfs- Add the nobody user to the nfs group:
root@debian:~# usermod -a -G nfs nobody- Create the directory to be shared:
root@debian:~# mkdir /nfs- Set permissions:
root@debian:~# chmod 770 /nfs && chgrp nfs /nfs- Edit
/etc/hostsand add the following entries:
192.168.1.100 nfs.std.local nfs
192.168.1.10 arch.std.local arch
192.168.1.11 debian.std.local debianNFS Service Configuration
- Edit
/etc/exportswith the following options:rw: enables read/write accesssync: ensures data is written to disk before a response is sentanongid: sets the anonymous group ID to 1001 (thenfsgroup created earlier). By default, UID and GID are 65534 (nobody)root_squash: prevents remote root users from acting as root on the exported shareno_subtree_check: disables subtree checking to improve reliability in certain cases
- Security modes (sec=...):
krb5: authentication only (no integrity or encryption)krb5i: authentication + integrity check (adds a hash to each request)krb5p: authentication + integrity + full encryption (most secure, highest CPU usage)
/nfs *(rw,sync,anongid=1001,root_squash,no_subtree_check,sec=krb5p)- For stronger security, restrict access by IP address filtering:
/nfs 192.168.1.10(rw,sync,anongid=1001,root_squash,no_subtree_check,sec=krb5p) 192.168.1.11(rw,sync,anongid=1001,root_squash,no_subtree_check,sec=krb5p)- Edit
/etc/default/nfs-kernel-serverto enable thesvcgssddaemon (required by Kerberos):
NEED_SVCGSSD="yes"- Restart the NFS service and export the share:
root@debian:~# systemctl restart nfs-kernel-server.service && exportfs -arvConfigure Kerberos
- Edit the Kerberos configuration file:
/etc/krb5.conf
[libdefaults]
default_realm = STD.LOCAL
kdc_timesync = 1
ccache_type = 4
forwardable = true
proxiable = true
fcc-mit-ticketflags = true
allow_weak_crypto = false
[realms]
STD.LOCAL = {
kdc = nfs.std.local
admin_server = nfs.std.local
default_domain = std.local
}
[domain_realm]
.std.local = STD.LOCAL
std.local = STD.LOCAL
[logging]
kdc = SYSLOG:NOTICE
admin_server = SYSLOG:NOTICE
default = SYSLOG:NOTICE- Create the Kerberos database and set the master key for the KDC:
root@debian:~# kdb5_util -r STD.LOCAL create -s
You will be prompted for the database Master Password.
It is important that you NOT FORGET this password.
Enter KDC database master key: MasterOfTheDomain:p
Re-enter KDC database master key to verify: MasterOfTheDomain:p- Edit
/etc/krb5kdc/kadm5.aclto define access control for Kerberos administration:
#*/admin@STD.LOCAL *
kdcadmin/admin@STD.LOCAL *- Start the following Kerberos services:
root@debian:~# systemctl start krb5-kdc.serviceroot@debian:~# systemctl start krb5-admin-server.service- Create an admin principal for Kerberos administration:
root@debian:~# kadmin.local
Authenticating as principal root/admin@STD.LOCAL with password.
kadmin.local: add_principal kdcadmin/admin@STD.LOCAL
No policy specified for kdcadmin/admin@STD.LOCAL; defaulting to no policy
Enter password for principal "kdcadmin/admin@STD.LOCAL":$superKDC$2000
Re-enter password for principal "kdcadmin/admin@STD.LOCAL":$superKDC$2000
Principal "kdcadmin/admin@STD.LOCAL" created.
kadmin: exit- Create an NFS user principal:
root@debian:~# kadmin.local
Authenticating as principal root/admin@STD.LOCAL with password.
kadmin.local: add_principal nfsuser@STD.LOCAL
No policy specified for nfsuser@STD.LOCAL; defaulting to no policy
Enter password for principal "nfsuser@STD.LOCAL":NFScher$$
Re-enter password for principal "nfsuser@STD.LOCAL":NFScher$$
Principal "nfsuser@STD.LOCAL" created.
kadmin: exit- Add NFS service principals for the server and clients:
root@debian:~# kadmin.local
kadmin.local: addprinc -randkey nfs/nfs.std.local@STD.LOCAL
No policy specified for nfs/nfs.std.local@STD.LOCAL; defaulting to no policy
Principal "nfs/nfs.std.local@STD.LOCAL" created.
kadmin.local: addprinc -randkey nfs/arch.std.local@STD.LOCAL
No policy specified for nfs/arch.std.local@STD.LOCAL; defaulting to no policy
Principal "nfs/arch.std.local@STD.LOCAL" created.
kadmin.local: addprinc -randkey nfs/debian.std.local@STD.LOCAL
No policy specified for nfs/debian.std.local@STD.LOCAL; defaulting to no policy
Principal "nfs/debian.std.local@STD.LOCAL" created.
kadmin: exit- Add NFS service principals to the
/etc/krb5.keytabfile:
root@debian:~# kadmin.local
kadmin.local: ktadd nfs/nfs.std.local
kadmin.local: ktadd nfs/arch.std.local
kadmin.local: ktadd nfs/debian.std.local
kadmin.local: exit- Restart the system to apply all changes (mandatory):
root@debian:~# rebootClient (ArchLinux)
- Install required packages:
[root@arch ~]# pacman -S nfs-utils- Enable the NFS client service at boot:
[root@arch ~]# systemctl enable nfs-client.target- Start the NFS client service:
[root@arch ~]# systemctl start nfs-client.target- Add host entries to
/etc/hosts:
192.168.1.100 nfs.std.local nfs
192.168.1.10 arch.std.local arch
192.168.1.11 debian.std.local debian- Edit
/etc/krb5.confto match the server configuration:
[libdefaults]
default_realm = STD.LOCAL
kdc_timesync = 1
ccache_type = 4
forwardable = true
proxiable = true
fcc-mit-ticketflags = true
allow_weak_crypto = false
[realms]
STD.LOCAL = {
kdc = nfs.std.local
admin_server = nfs.std.local
default_domain = std.local
}
[domain_realm]
.std.local = STD.LOCAL
std.local = STD.LOCALAdd the nfs/arch.std.local entry to /etc/krb5.keytab
You can either copy the /etc/krb5.keytab file from the server, or generate it on the client using Kerberos.
- Generate it from the client using Kerberos:
[root@arch ~]# kadmin -p kdcadmin/admin@STD.LOCAL
Authenticating as principal kdcadmin/admin@STD.LOCAL with password.
Password for kdcadmin/admin@STD.LOCAL: $superKDC$2000
kadmin: ktadd nfs/arch.std.local
Entry for principal nfs/arch.std.local with kvno 3, encryption type aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96 added to keytab FILE:/etc/krb5.keytab.
Entry for principal nfs/arch.std.local with kvno 3, encryption type aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96 added to keytab FILE:/etc/krb5.keytab.
kadmin: exit- Restart the system:
[root@arch ~]# reboot- Create the mount point and mount the NFS share:
[root@arch ~]# mkdir /mnt/nfs[root@arch ~]# mount -t nfs -o sec=krb5p nfs.std.local:/nfs /mnt/nfs/- Obtain a Kerberos ticket:
[user@arch ~]$ kinit nfsuser@STD.LOCAL
Password for nfsuser@STD.LOCAL: NFScher$$You now have access to the NFS share as a regular user.
- Verify the Kerberos ticket:
[user@arch ~]$ klist
Ticket cache: FILE:/tmp/krb5cc_1000
Default principal: nfsuser@STD.LOCAL
Valid starting Expires Service principal
18/09/2022 20:14:38 19/09/2022 06:14:38 krbtgt/STD.LOCAL@STD.LOCAL
renew until 19/09/2022 15:14:33- To allow users to mount the share manually after authentication, add this to
/etc/fstab:
nfs.std.local:/nfs /mnt/nfs nfs defaults,timeo=900,retrans=5,_netdev,sec=krb5p,user,noauto 0 0Client (Debian)
- Install required packages:
root@debian:~# apt update && apt install nfs-common krb5-user- Enable the NFS client service at boot:
root@debian:~# systemctl enable nfs-client.target- Start the NFS client service:
root@debian:~# systemctl start nfs-client.target- Add host entries to
/etc/hosts:
192.168.1.100 nfs.std.local nfs
192.168.1.10 arch.std.local arch
192.168.1.11 debian.std.local debian- Edit
/etc/krb5.confto match the server configuration:
[libdefaults]
default_realm = STD.LOCAL
kdc_timesync = 1
ccache_type = 4
forwardable = true
proxiable = true
fcc-mit-ticketflags = true
allow_weak_crypto = false
[realms]
STD.LOCAL = {
kdc = nfs.std.local
admin_server = nfs.std.local
default_domain = std.local
}
[domain_realm]
.std.local = STD.LOCAL
std.local = STD.LOCALAdd the nfs/debian.std.local entry to /etc/krb5.keytab
You can either copy the /etc/krb5.keytab file from the server, or generate it on the client using Kerberos.
- Generate it from the client using Kerberos:
root@debian:~# kadmin -p kdcadmin/admin@STD.LOCAL
Authenticating as principal kdcadmin/admin@STD.LOCAL with password.
Password for kdcadmin/admin@STD.LOCAL: $superKDC$2000
kadmin: ktadd nfs/debian.std.local
Entry for principal nfs/debian.std.local with kvno 3, encryption type aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96 added to keytab FILE:/etc/krb5.keytab.
Entry for principal nfs/debian.std.local with kvno 3, encryption type aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96 added to keytab FILE:/etc/krb5.keytab.
kadmin: exit- Restart the system:
[root@arch ~]# reboot- Mount the NFS share to
/mnt:
[root@arch ~]# mkdir /mnt/nfs[root@arch ~]# mount -t nfs -o sec=krb5p nfs.std.local:/nfs /mnt/nfs/- Request a Kerberos ticket:
[user@arch ~]$ kinit nfsuser@STD.LOCAL
Password for nfsuser@STD.LOCAL: NFScher$$The user now has access to the NFS share.
- Check Kerberos ticket status:
[user@arch ~]$ klist
Ticket cache: FILE:/tmp/krb5cc_1000
Default principal: nfsuser@STD.LOCAL
Valid starting Expires Service principal
09/21/2022 18:12:01 09/22/2022 04:12:01 krbtgt/STD.LOCAL@STD.LOCAL
renew until 09/22/2022 18:11:39
09/21/2022 18:12:03 09/22/2022 04:12:01 nfs/nfs.std.local@STD.LOCAL
renew until 09/22/2022 18:11:39- To allow the user to mount
/mnt/nfsafter Kerberos authentication, add the following line to/etc/fstab:
nfs.std.local:/nfs /mnt/nfs nfs defaults,timeo=900,retrans=5,_netdev,sec=krb5p,user,noauto 0 0Miscellaneous
Commands
- Save a specific key to a
keytabfile:
root@debian:~# ktadd -k krb5.keytab nfs/archtoi.std.local- List cached Kerberos tickets:
root@debian:~# klist- Destroy Kerberos tickets:
root@debian:~# kdestroy- Renew a Kerberos ticket:
root@debian:~# kinit -R- List existing Kerberos principals:
root@debian:~# kadmin.local
Authenticating as principal root/admin@STD.LOCAL with password.
kadmin.local: listprincs
K/M@STD.LOCAL
kadmin/admin@STD.LOCAL
kadmin/changepw@STD.LOCAL
kadmin/nfskerb@STD.LOCAL
kdcadmin/admin@STD.LOCAL
kiprop/nfskerb@STD.LOCAL
krbtgt/STD.LOCAL@STD.LOCAL
nfs/arch.std.local@STD.LOCAL
nfs/debian.std.local@STD.LOCAL
nfs/nfs.std.local@STD.LOCAL
nfsuser@STD.LOCAL- Remove Kerberos principals:
root@debian:~# kadmin.local
Authenticating as principal root/admin@STD.LOCAL with password.
kadmin.local: delete_principal nfs/arch.std.local@STD.LOCA- List entries in
/etc/krb5.keytab:
root@debian:~# klist -e -k /etc/krb5.keytab
Keytab name: FILE:/etc/krb5.keytab
KVNO Principal
---- --------------------------------------------------------------------------
4 nfs/debian.std.local@STD.LOCAL (aes256-cts-hmac-sha1-96)
4 nfs/debian.std.local@STD.LOCAL (aes128-cts-hmac-sha1-96)- List entries in
/etc/krb5.keytab(alternative):
root@debian:~# ktutil
ktutil: rkt /etc/krb5.keytab
ktutil: list
slot KVNO Principal
---- ---- ---------------------------------------------------------------------
1 2 nfs/nfs.std.local@STD.LOCAL
2 2 nfs/nfs.std.local@STD.LOCAL
3 2 nfs/arch.std.local@STD.LOCAL
4 2 nfs/arch.std.local@STD.LOCAL
5 2 nfs/debian.std.local@STD.LOCAL
6 2 nfs/debian.std.local@STD.LOCAL- Delete an entry from
/etc/krb5.keytabusingktutil:
root@debian:~# ktutil
ktutil: delete_entry nfs/arch.std.local@STD.LOCALSetting Up a Firewall for the Server (Optional)
This section details the nftables rules used to secure the NFS and Kerberos server.
Ports Used
- The following ports are required for NFS and Kerberos services:
| Service | TCP | UDP |
|---|---|---|
| Kerberos | 88, 749 | 88, 749 |
| NFSv4 | 2049 |
Disable IPv6
- Edit
/etc/sysctl.confand add the following lines:
net.ipv6.conf.all.disable_ipv6=1
net.ipv6.conf.all.autoconf=0
net.ipv6.conf.default.disable_ipv6=1
net.ipv6.conf.default.autoconf=0- Apply the changes:
root@debian:~# sysctl -p /etc/sysctl.confnftables
- Enable the nftables service:
root@debian:~# systemctl enable nftables.service- Edit the
/etc/nftables.conffile:
#!/usr/sbin/nft -f
flush ruleset
# ----- IPv4 -----
table ip filter {
chain INPUT {
type filter hook input priority 0; policy drop; #by default, we drop traffic
iif lo accept comment "Accept any localhost traffic"
ct state invalid counter drop comment "Drop invalid connections"
ct state { established, related } counter accept comment "Accept traffic originated from us"
iif != lo ip daddr 127.0.0.1/8 counter drop comment "drop connections to loopback not coming from loopback"
tcp flags & (fin | syn | rst | psh | ack | urg) > urg counter drop comment "Drop TCP Null"
tcp flags & (fin | syn | rst | psh | ack | urg) < fin counter drop comment "Drop TCP XMS"
ip protocol icmp icmp type { destination-unreachable, router-solicitation, router-advertisement, time-exceeded, parameter-problem, echo-request } accept comment "Accept ICMP"
iif ens192 ip saddr { 192.168.1.10, 192.168.1.11 } tcp dport { ssh, 88, 749, 2049 } counter accept comment "Accept ssh, kerberos tcp and nfsv4"
iif ens192 ip saddr { 192.168.1.10, 192.168.1.11 } udp dport { 88, 749 } counter accept comment "Accept kerberos udp"
iif ens192 tcp sport { http, https, 53, ntp } counter accept comment "Accept http, https, dns and ntp TCP"
iif ens192 udp sport { 53, ntp } counter accept comment "Accept dns and ntp UDP"
log counter drop #log (/var/log/kern.log), count and drop any other rules
}
chain FORWARD {
type filter hook forward priority 0; policy drop;
counter comment "count dropped packets"
}
chain OUTPUT {
type filter hook output priority 0; policy drop;
oif ens192 ip daddr { 192.168.1.10, 192.168.1.11 } tcp sport { ssh, 88, 749, 2049 } counter accept comment "Accept ssh, kerberos tcp and nfsv4"
oif ens192 ip daddr { 192.168.1.10, 192.168.1.11 } udp sport { 88, 749 } counter accept comment "Accept kerberos udp"
tcp dport { http, https, 53, ntp } counter accept comment "Accept http, https, dns and ntp TCP"
udp dport { 53, ntp } counter accept comment "Accept dns and ntp UDP"
ip protocol icmp icmp type { destination-unreachable, router-solicitation, router-advertisement, time-exceeded, parameter-problem, echo-request, echo-reply } accept comment "Accept ICMP"
log counter drop #log (/var/log/kern.log), count and drop any other rules
}
}- Restart the nftables service to apply the rules:
root@debian:~# systemctl restart nftables.service