Deploy Elastic 9 (Elasticsearch + Kibana) on Debian for Centralized Log Monitoring
- Last updated: Apr 28, 2025
In this article, I will show you how to install Elastic, a SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) solution developed by Elastic NV. A SIEM is a cybersecurity platform that centralizes and analyzes logs and events from multiple devices across a network, enabling the detection of anomalous activities and the generation of alerts in real time.
We will install the full Elastic stack, which includes Elasticsearch and Kibana, on a Debian server deployed on-premises — meaning no license purchase is required for basic use. However, I always recommend that companies consider subscribing to a commercial license for full support and additional features. I had previously published an article covering the installation of Elastic Stack version 8 (available here), and with the release of version 9, I am taking this opportunity to update the guide accordingly.
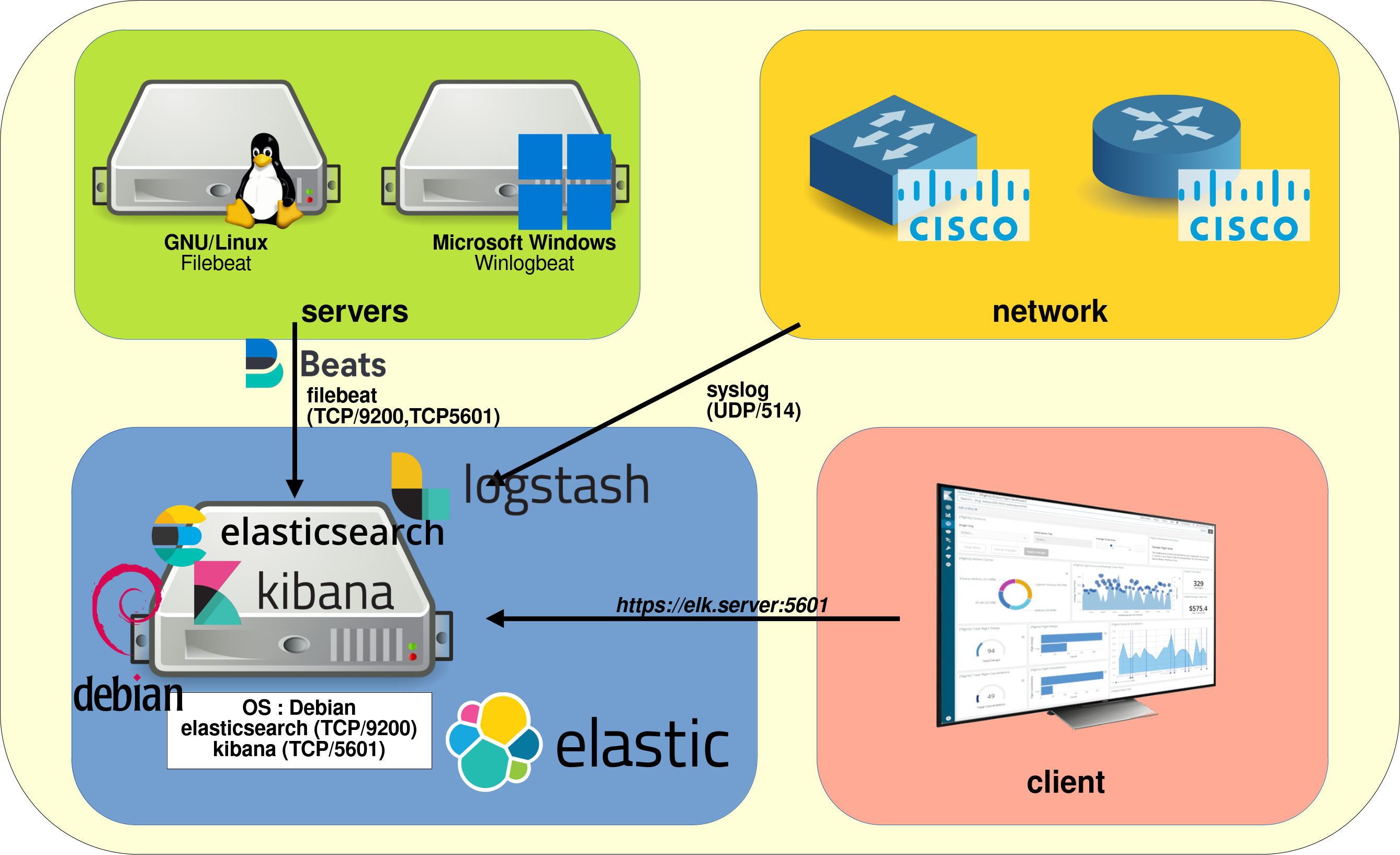
Elastic Stack Architecture
Elasticsearch is a real-time, distributed storage, search, and analytics engine.
Kibana is an open source analytics and visualization platform designed to work with Elasticsearch. Kibana will be used to search, view, and interact with data stored in Elasticsearch indices.
Notes
Versions
- OS: Debian
- Elasticsearch: 9
Links
- Download link : https://www.elastic.co/
- Official guide : https://www.elastic.co/docs/deploy-manage/deploy/self-managed/install-elasticsearch-with-debian-package
- Elastic Stack Editions https://www.elastic.co/subscriptions
The components of Elastic
Main
- Elasticsearch: Distributed, RESTful search and analytics.
- Kibana: Visualize your data. Navigate the Stack.
- Beats: Collect, parse, and ship in a lightweight fashion.
Others
- Logstash: Ingest, transform, enrich, and output.
- Filebeat: Real-time insight into log data.
Ports used
- ElastiSearch default port:
http://IP_ADDRESS:9200 - Kibana web access:
http://IP_ADDRESS:5601 - Logstash default port:
9600
Installing Elastic (Debian Server)
Prerequisites
- Install
apt-transport-httpsand prerequisite packages:
root@host:~# apt update && apt install apt-transport-https gnupg curl wget- Import the Elasticsearch PGP key:
root@host:~# wget -qO - https://artifacts.elastic.co/GPG-KEY-elasticsearch | gpg --dearmor -o /usr/share/keyrings/elasticsearch-keyring.gpg- Save the repository definition:
root@host:~# echo "deb [signed-by=/usr/share/keyrings/elasticsearch-keyring.gpg] https://artifacts.elastic.co/packages/9.x/apt stable main" | tee /etc/apt/sources.list.d/elastic-9.x.listElasticsearch
- Install Elasticsearch and note the superuser password:
root@host:~# apt update && apt install elasticsearch[…]
--------------------------- Security autoconfiguration information ------------------------------
Authentication and authorization are enabled.
TLS for the transport and HTTP layers is enabled and configured.
The generated password for the elastic built-in superuser is : elastic_password;)
If this node should join an existing cluster, you can reconfigure this with
'/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-reconfigure-node --enrollment-token <token-here>
after creating an enrollment token on your existing cluster.
You can complete the following actions at any time:
Reset the password of the elastic built-in superuser with
'/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-reset-password -u elastic'.
Generate an enrollment token for Kibana instances with
'/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-create-enrollment-token -s kibana'.
Generate an enrollment token for Elasticsearch nodes with
'/usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-create-enrollment-token -s node'.
-------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Kibana
- Install Kibana:
root@host:~# apt update && apt install kibanaConfiguring
Elasticsearch
- Edit
/etc/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.ymlto set the bind address to all:
network.host: 0.0.0.0- Start the elasticsearch service:
root@host:~# systemctl start elasticsearch.service- Check the elastic service is running:
root@host:~# curl --cacert /etc/elasticsearch/certs/http_ca.crt -u elastic https://localhost:9200
Enter host password for user 'elastic': elastic_password;)
{
"name" : "std",
"cluster_name" : "elasticsearch",
"cluster_uuid" : "StdgreaTBanDKphU4S0ceg",
"version" : {
"number" : "9.0.0",
"build_flavor" : "default",
"build_type" : "deb",
"build_hash" : "112859b85d50de2a7e63f73c8fc70b99eea24291",
"build_date" : "2025-04-08T15:13:46.049795831Z",
"build_snapshot" : false,
"lucene_version" : "10.1.0",
"minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "8.18.0",
"minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "8.0.0"
},
"tagline" : "You Know, for Search"
}Kibana
- Edit
/etc/kibana/kibana.ymlto set the bind address to all:
server.host: "0.0.0.0"
server.publicBaseUrl: "http://X.X.X.X:5601"- Start service:
root@host:~# systemctl start kibana.service- Create an enrollment token:
root@host:~# /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-create-enrollment-token -s kibana
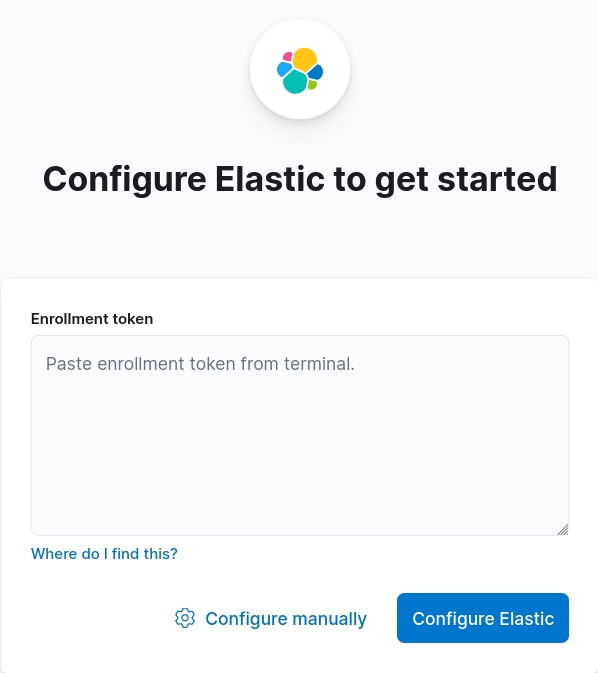
eyJ2ZXIiOiI4LjEuMiIsImFkciI6WyIxOTIuMTY4LjEuNjY6OTIwMCJdLCJmZ3IiOiJmYzdiZmFmMjNmODEzN2M1NmY4YTg1NGMxNTdjMWFkYTNiZDdiOGM4NTE4YTZhNmI3wWNiYzBkNzc0ZTRjNzc1Iiwia2V5Ijoib1ZBTkVJQUIxWVNBT0BiUWVsUVc6cEU1WXF3U1FTUENjcFFaZUJvTGtKdyJ0- From Firefox open
http://X.X.X.X:5601and paste enrollment token then click to Configure Elastic:
- Generate Kibana verification code and paste it:
root@host:~# /usr/share/kibana/bin/kibana-verification-code
Your verification code is: 139 477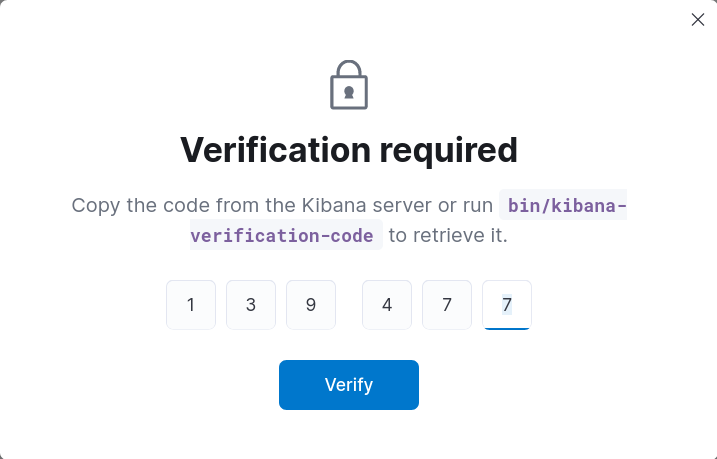
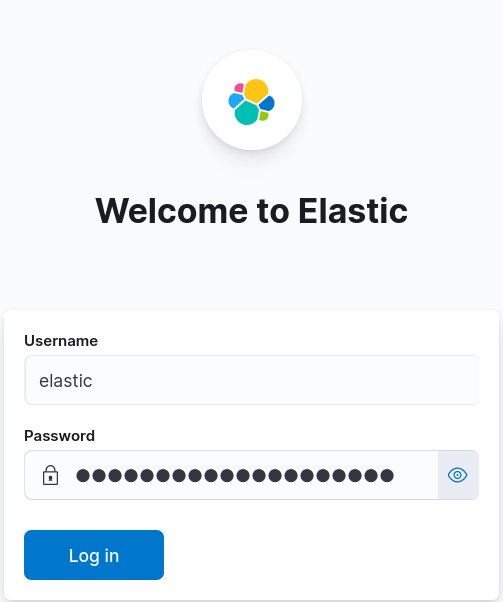
- Now we can connect to Kibana with the elastic account:
Securing Kibana
Since version 8, Elasticsearch is automatically configured to encrypt its communications.
This is not the case with Kibana for which we connect using http. We will see how to enable HTTPS connections.
- Run the
kibana-encryption-keysscript and copy the values below settings:
root@host:~# /usr/share/kibana/bin/kibana-encryption-keys generate
## Kibana Encryption Key Generation Utility
The 'generate' command guides you through the process of setting encryption keys for:
xpack.encryptedSavedObjects.encryptionKey
Used to encrypt stored objects such as dashboards and visualizations
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/xpack-security-secure-saved-objects.html#xpack-security-secure-saved-objects
xpack.reporting.encryptionKey
Used to encrypt saved reports
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/reporting-settings-kb.html#general-reporting-settings
xpack.security.encryptionKey
Used to encrypt session information
https://www.elastic.co/guide/en/kibana/current/security-settings-kb.html#security-session-and-cookie-settings
Already defined settings are ignored and can be regenerated using the --force flag. Check the documentation links for instructions on how to rotate encryption keys.
Definitions should be set in the kibana.yml used configure Kibana.
Settings:
xpack.encryptedSavedObjects.encryptionKey: caeb7879368e3dd66d7302f6810daec1
xpack.reporting.encryptionKey: c1c89f500966ac710f7fa5eaf2939976
xpack.security.encryptionKey: e1458d710ffb321e4a4f4eb792c78b2b- Put the previous copied informations to
/etc/kibana/kibana.yml:
[…]
xpack.encryptedSavedObjects.encryptionKey: caeb7879368e3dd66d7302f6810daec1
xpack.reporting.encryptionKey: c1c89f500966ac710f7fa5eaf2939976
xpack.security.encryptionKey: e1458d710ffb321e4a4f4eb792c78b2b- Get the secure password of the
http.p12container:
root@host:~# /usr/share/elasticsearch/bin/elasticsearch-keystore show xpack.security.http.ssl.keystore.secure_password
592l_UJGSXmliJIvuokDab- Extract necessary certificates to
/etc/kibana/:
root@host:~# cd /etc/kibana/root@host:~# openssl pkcs12 -in /etc/elasticsearch/certs/http.p12 -out server.crt -clcerts -nokeys
Enter Import Password:592l_UJGSXmliJIvuokDabroot@host:~# openssl pkcs12 -in /etc/elasticsearch/certs/http.p12 -out server.key -nocerts -nodes
Enter Import Password:592l_UJGSXmliJIvuokDabroot@host:~# chown root:kibana /etc/kibana/server.*root@host:~# chmod g+r /etc/kibana/server.*- Edit the
/etc/kibana/kibana.ymlfile:
server.ssl.enabled: true
server.ssl.certificate: /etc/kibana/server.crt
server.ssl.key: /etc/kibana/server.key- Restart the kibana service:
root@host:~# systemctl restart kibana.serviceWait some seconds and connect to kibana at https://X.X.X.X:5601
Autostart
To make our Elasticsearch and Kibana services start at boot, we need to do some modifications.
Elasticsearch
- Set Elasticsearch service to start when the server starts:
root@host:~# systemctl enable elasticsearch.serviceKibana
- Set Kibana service to start when the server starts:
root@host:~# systemctl enable kibana.serviceView Logs
Elasticsearch
- We can display logs from the
elasticsearch.logfile:
root@host:~# tail /var/log/elasticsearch/elasticsearch.log- Or with the
journalctlcommand:
root@host:~# journalctl --unit elasticsearchKibana
- We can display logs from the
kibana.logfile:
root@host:~# tail /var/log/kibana/kibana.log- Or with the
journalctlcommand:
root@host:~# journalctl --unit kibanaWe now have a fully operational Elastic solution. The next step is to deploy modules to enable our servers and network devices to forward their logs for centralized analysis.