Secure SSH on Linux with nftables Firewall
- Last updated: Aug 20, 2025

In a previous article, I explained how to secure SSH with two-factor authentication (2FA). In addition to 2FA, you can strengthen SSH security by using the netfilter firewall, managed with nftables. This approach allows you to restrict access so that only trusted IP addresses can connect to your Linux server. Both protections, 2FA and nftables, are complementary and can be combined for maximum security.
Setting up nftables rules for SSH is relatively simple, so there is no reason not to implement them.
This method is especially useful if only a few known IP addresses should be allowed to connect. You can also apply Geo-Filtering, restricting access by country or region using the IPdeny IP address lists as we will see in the last part of this tutorial.
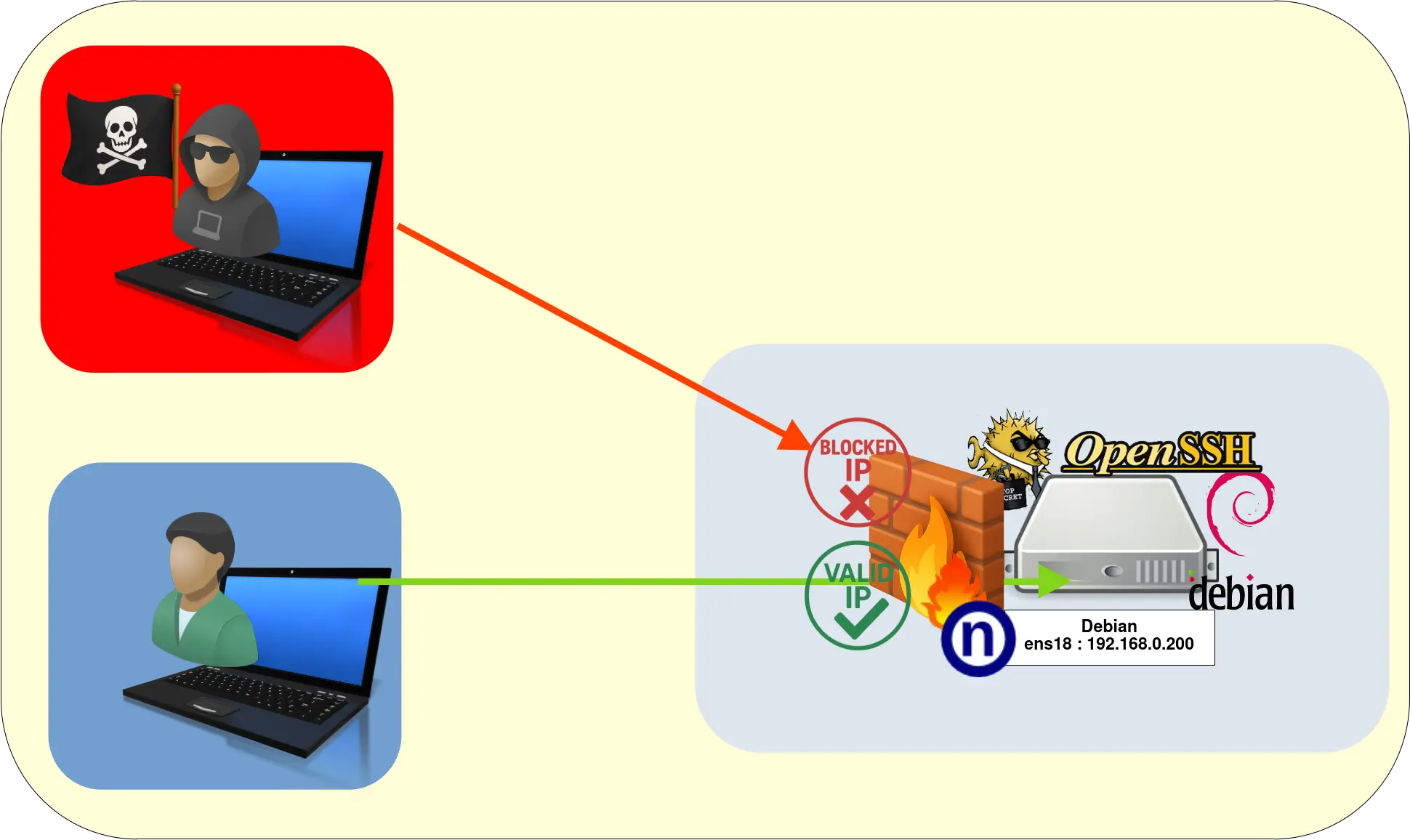
Allow SSH Access with an IP Whitelist
For example, imagine we only want to allow access from our local network (192.168.0.0/24) and two specific public IP addresses: 198.51.100.51 and 2001:db8:51d:dead:bee5::1. All other IPs will be blocked.
SSH Whitelist Firewall Diagram
Configuring the /etc/nftables.conf File for SSH
- Edit the
/etc/nftables.conffile:
#!/usr/sbin/nft -f
flush ruleset
table inet filter {
chain input {
type filter hook input priority filter; policy accept; # Default: accept all
iif lo accept comment "Accept any localhost traffic"
ip saddr { 192.168.0.0/24, 198.51.100.51 } tcp dport { ssh } ct state { new, related, established } counter accept comment "Allow SSH from specific IPv4"
ip6 saddr { 2001:db8:51d:dead:bee5::1 } tcp dport { ssh } ct state { new, related, established } counter accept comment "Allow SSH from specific IPv6"
tcp dport { ssh } ct state { new, related, established } counter drop comment "Block all other SSH attempts"
}
chain forward {
type filter hook forward priority filter; policy accept; # Default: accept all
}
chain output {
type filter hook output priority filter; policy accept; # Default: accept all
}
}- After editing the
/etc/nftables.conffile, load thenftablesrules:
root@debian:~# nft -f /etc/nftables.conf- Enable the
nftablesservice so that it starts automatically at boot:
root@debian:~# systemctl enable nftables.serviceAllow SSH Access with Geo‑IP Restrictions
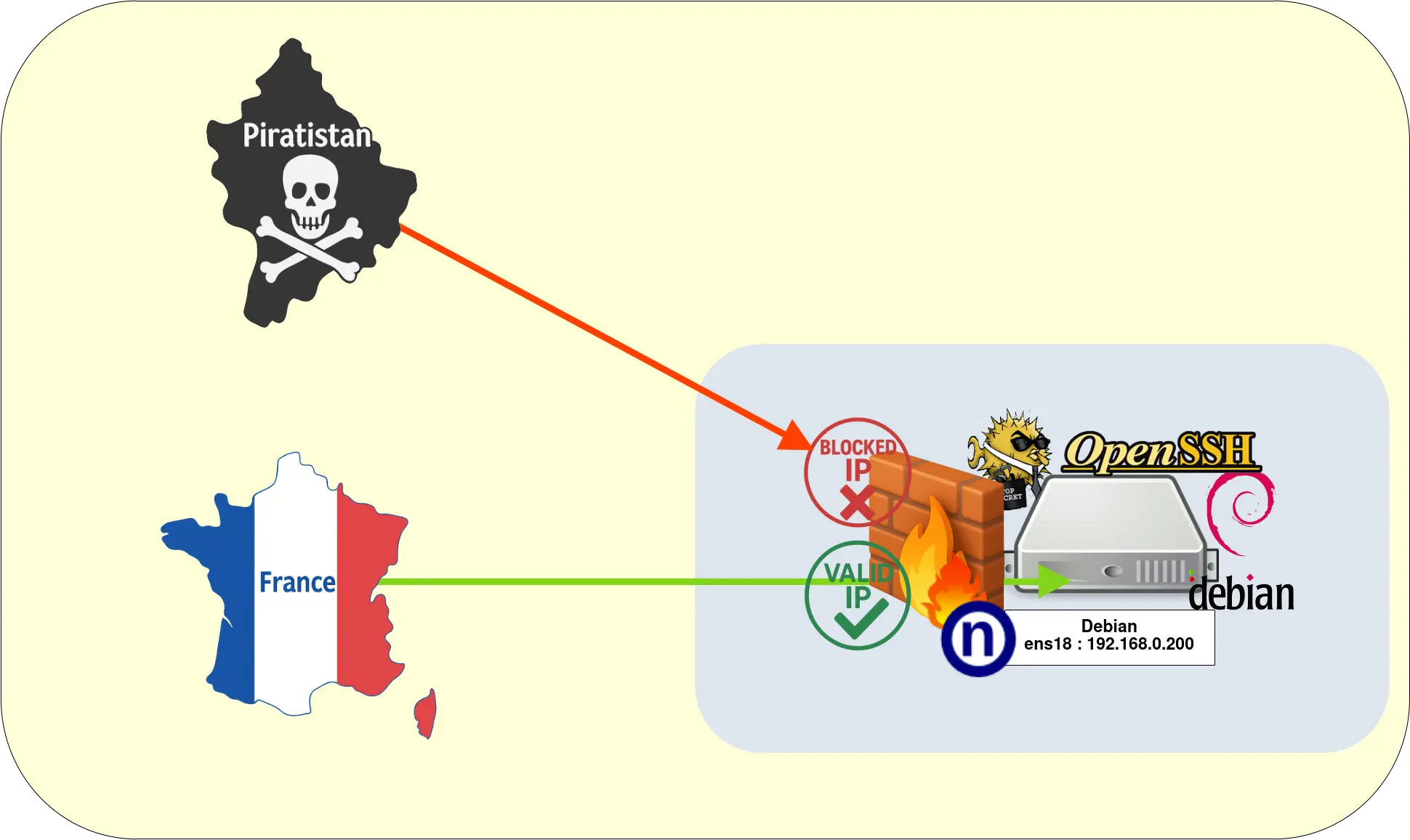
As explained in the introduction, we will use the IPdeny lists to apply Geo-IP filtering. The IPdeny lists are freely available collections of IP address ranges grouped by country or region, which can be used to allow or block network traffic based on geographic location.
In this example, we only want to allow SSH connections from France 😇 (both IPv4 and IPv6). We will start by downloading the France IPv4 list and the France IPv6 list.
SSH Geo‑IP Filtering Diagram
Download and Format IPdeny Lists for Geo-IP Filtering
We need to format our IP list file so that it matches the syntax expected by nftables. For example, the IPv6 list for France🇫🇷 should look like this:
set fr_aggregated_v6 {
type ipv6_addr
flags interval
elements = {
2001:0504:0118:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000/48,
2001:0660:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000/29,
2a14:f100:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000/29,
2a14:f400:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000/29,
2a14:fa80:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000/29
}
}By default, the IPdeny lists are provided in a raw format, like this:
2001:0504:0118:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000/48
2001:0660:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000/29
2a14:f100:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000/29
2a14:f400:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000/29
2a14:fa80:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000:0000/29But don't panic — I will show below how to reformat the IPdeny lists step by step!
- First, download the list with
wgetand save it asfr-aggregated-v4.zoneandfr-aggregated-v6.zone. For example, here is the commands for the French IPs:
root@debian:~# wget https://www.ipdeny.com/ipblocks/data/aggregated/fr-aggregated.zone -O fr-aggregated-v4.zoneroot@debian:~# wget https://www.ipdeny.com/ipv6/ipaddresses/aggregated/fr-aggregated.zone -O fr-aggregated-v6.zoneDepending on the country you want to allow, you may notice that there are a large number of lines to format. Fortunately, we can use the sed command to automate this task.
- For the IPv4 list (
fr-aggregated-v4.zone), use the following command:
root@debian:~# sed -i -e 's/$/,/' -e '${s/,$/\n }\n}/}' -e '1s/^/set fr_aggregated_v4 {\n type ipv4_addr\n flags interval\n elements = {\n/' fr-aggregated-v4.zone- For the IPv6 list (
fr-aggregated-v6.zone), use the following command:
root@debian:~# sed -i -e 's/$/,/' -e '${s/,$/\n }\n}/}' -e '1s/^/set fr_aggregated_v6 {\n type ipv6_addr\n flags interval\n elements = {\n/' fr-aggregated-v6.zone- Finally, move the
fr-aggregated-v4.zoneandfr-aggregated-v6.zonefiles into the/etc/nftablesdirectory (create it first if it does not exist):
root@debian:~# mkdir -p /etc/nftablesroot@debian:~# mv fr-aggregated-v4.zone fr-aggregated-v6.zone -t /etc/nftablesAdding Geo-IP SSH Rules to /etc/nftables.conf
- Next, add the lists to the
/etc/nftables.conffile by editing it as follows:
#!/usr/sbin/nft -f
flush ruleset
table inet filter {
include "/etc/nftables/fr-aggregated-v4.zone"
include "/etc/nftables/fr-aggregated-v6.zone"
chain input {
type filter hook input priority filter; policy accept; # Default: accept all
iif lo accept comment "Allow localhost traffic"
ip saddr { 192.168.0.0/24 } tcp dport { ssh } ct state { new, related, established } counter accept comment "Allow SSH from LAN"
ip saddr @fr_aggregated_v4 tcp dport { ssh } ct state { new, related, established } counter accept comment "Allow SSH from France (IPv4)"
ip6 saddr @fr_aggregated_v6 tcp dport { ssh } ct state { new, related, established } counter accept comment "Allow SSH from France (IPv6)"
tcp dport { ssh } ct state { new, related, established } counter drop comment "Block SSH from any other IP"
}
chain forward {
type filter hook forward priority filter; policy accept; # Default: accept all
}
chain output {
type filter hook output priority filter; policy accept; # Default: accept all
}
}As with the IP Whitelist example, once you have edited the /etc/nftables.conf file, follow these steps:
- Load the new
nftablesrules:
root@debian:~# nft -f /etc/nftables.conf- Enable the
nftablesservice so that it starts automatically at boot:
root@debian:~# systemctl enable nftables.service