Configuration d'un VPN IPsec multisite avec StrongSwan sur Debian
- Mise à jour le 19 janv. 2025

J'ai déjà détaillé dans un article précédent comment configurer un VPN IPsec multisite en combinant Racoon et strongSwan ici : Comment configurer un VPN IPsec multisite avec Racoon et strongSwan. Comme Racoon est désormais obsolète, je vais décrire ici comment configurer une architecture de VPN IPsec multisite, mais uniquement avec strongSwan.
- L'architecture présentée dans ce guide se compose de trois routeurs sur lesquels sont installés Debian et strongSwan :
- Le site principal (headquarters) : le cœur de l'architecture, il comprend quatre réseaux, pour les utilisateurs, les téléphones IP, le WiFi et les serveurs d'applications pour les utilisateurs internes et ceux des autres sites (agence 1 et 2). Il est également utilisé comme passerelle VPN pour le trafic entre Agence 1 et Agence 2.
- Agence 1 (Branch Office 1) : composée de trois réseaux : pour les utilisateurs, les téléphones IP et le WiFi.
- Agence 2 (Branch Office 2) : composée de trois réseaux : pour les utilisateurs, les téléphones IP et le WiFi.
- Avant de commencer :
- Nous aurions pu ajouter un tunnel IPsec entre l'Agence 1 et l'Agence 2 au lieu d'utiliser le Siège comme passerelle VPN. Cependant, comme le trafic entre les deux agences est peu significatif (uniquement des communications téléphoniques IP), je n'ai pas opté pour cette solution.
Schéma réseau
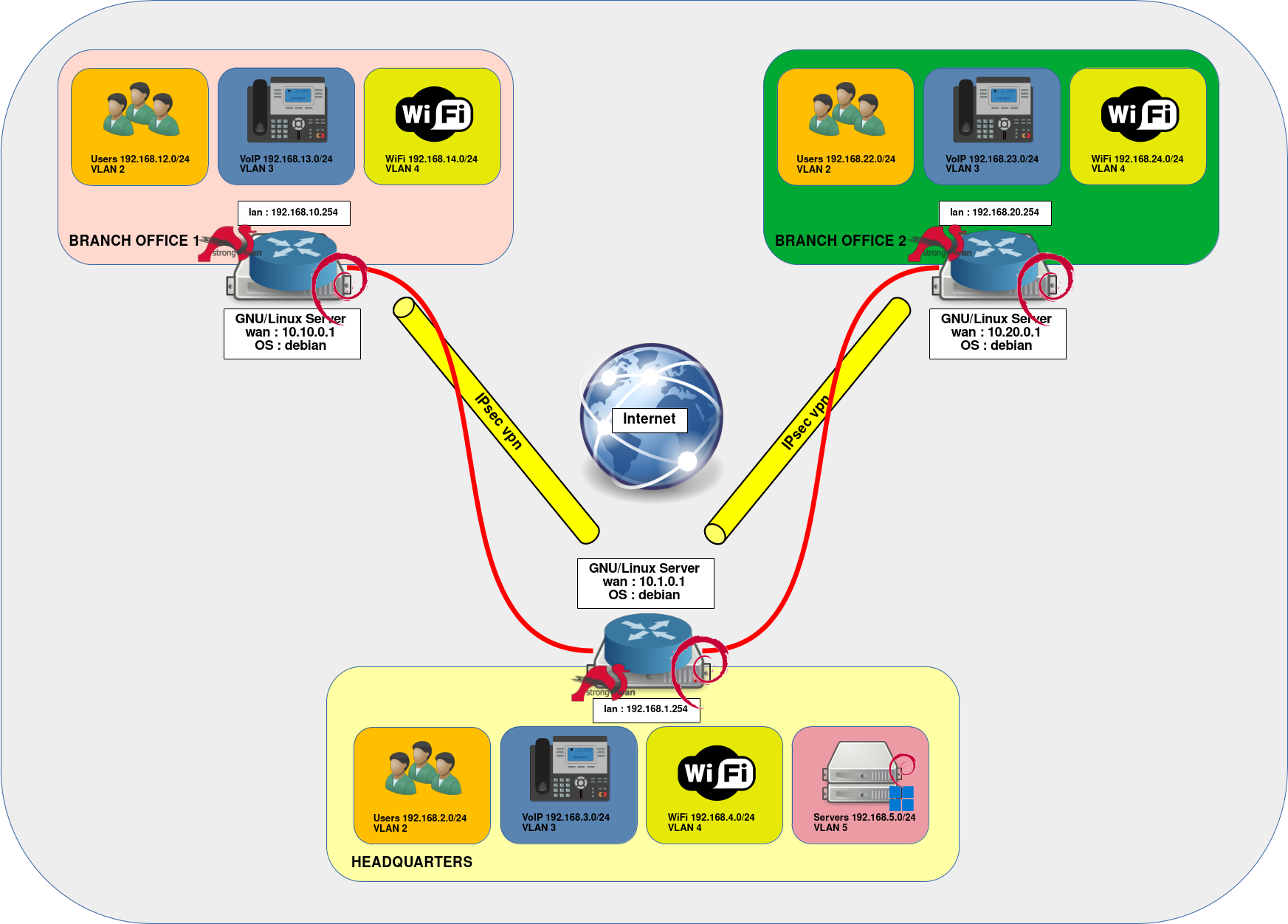
Site 1 - Headquarters
Commençons par la configuration du site principal. Pour rappel, il s'agit du site qui centralise les connexions VPN pour tous les autres sites, et c'est également le site qui "autorise" les connexions (le réseau VoIP dans cette configuration) entre Agence 1 et Agence 2.
Prérequis
- Installer le paquet strongSwan :
root@host:~# apt update && apt install strongswan- Activer le démarrage automatique de
nftables:
root@host:~# systemctl enable nftables.servicenftables
La configuration de nftables est ici ultra-simplifiée, permettant aux réseaux d'accéder à Internet et de communiquer entre eux. Dans un environnement de production, vous pouvez mettre en place un filtrage entre les VLANs.
- Modifier le fichier
/etc/nftables.conf:
#!/usr/sbin/nft -f
flush ruleset
table inet filter {
chain input {
type filter hook input priority 0; policy accept;
}
chain forward {
type filter hook forward priority 0; policy accept ;
}
chain output {
type filter hook output priority 0; policy accept;
}
}
#NAT for outgoing traffic.
table ip my_nat {
chain my_masquerade {
type nat hook postrouting priority 100;
ip daddr != { 10.1.0.1, 192.168.0.0/16 } oifname wan masquerade comment "output nat"
}
}- Recharger la configuration de
nftables:
root@host:~# nft -f /etc/nftables.confConfiguration réseau
Configurer les interfaces réseau
Ici, nous configurons nos deux interfaces : lan et wan (Lisez cet article pour découvrir comment renommer les interfaces réseau sous Debian : Renommer les interfaces réseau sur Debian).
- Modifier le fichier
/etc/network/interfaces:
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# and how to activate them. For more information, see interfaces(5).
source /etc/network/interfaces.d/*
# The loopback network interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# The primary network interface
# This is an autoconfigured IPv6 interface
allow-hotplug wan
iface wan inet static
address 10.1.0.1
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 10.1.0.254
allow-hotplug lan
iface lan inet static
address 192.168.1.254
netmask 255.255.255.0
up /usr/local/sbin/ipconf.sh- Redémarrez le système ou le service réseau :
root@host:~# systemctl restart networkingScript réseau
Le script /usr/local/sbin/ipconf.sh sera exécuté au démarrage. Il est utilisé pour configurer les interfaces VLAN.
- Créer un fichier
/usr/local/sbin/ipconf.sh:
#!/bin/sh
#SETTING UP VLANs ON THE lan INTERFACE
ip link add link lan name users type vlan id 2
ip link add link lan name voip type vlan id 3
ip link add link lan name wifi type vlan id 4
ip link add link lan name servers type vlan id 5
ip link set users up
ip link set voip up
ip link set wifi up
ip link set servers up
#VLAN INTERFACE IP ADDRESS SETTINGS
ip addr add 192.168.2.254/24 dev users
ip addr add 192.168.3.254/24 dev voip
ip addr add 192.168.4.254/22 dev wifi
ip addr add 192.168.5.254/24 dev servers
#ENABLE ROUTING
sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward=1- Modifier les droits du fichier
/usr/local/sbin/ipconf.shpour le rendre exécutable :
root@host:~# chmod +x /usr/local/sbin/ipconf.shstrongSwan
ipsec.conf
- Modifier le fichier
/etc/ipsec.confet configurer les connexions entre les sites. L'objectif est de permettre aux réseaux VoIP de tous les sites de communiquer entre eux. Nous permettons également aux utilisateurs de l'Agence 1 et de l'Agence 2 d'accéder au réseau des serveurs du Siège :
#####################################
#Headquarters to Branch Office 1 setup#
#####################################
conn hq-b1
authby = secret
auto = route
type = tunnel
keyexchange = ikev2
ike = aes256-sha256-modp1024!
esp = aes256-sha256-modp1024!
#DPD
dpdaction=restart
dpddelay=300s
dpdtimeout=60s
#headquarters
leftfirewall = yes
leftid = 10.1.0.1
left = 10.1.0.1
leftsubnet = 192.168.1.0/24
#Branch Office 1
rightfirewall = yes
rightid = 10.10.0.1
right = 10.10.0.1
rightsubnet = 192.168.10.0/24
#VoIP - Headquarters and Branch Office 1
conn hq-b1-voip
also=hq-b1
leftsubnet = 192.168.3.0/24
rightsubnet = 192.168.13.0/24
#Servers/Headquarters and Users/Branch Office 1
conn hq-b1-servers
also=hq-b1
leftsubnet = 192.168.5.0/24
rightsubnet = 192.168.12.0/24
#VoIP/Branch Office 1 - Headquarters - VoIP/Branch Office 2
conn b1-hq-b2-voip
also=hq-b1
leftsubnet = 192.168.23.0/24
rightsubnet = 192.168.13.0/24
#####################################
#Headquarters to Branch Office 2 setup#
#####################################
conn hq-b2
authby = secret
auto = route
type = tunnel
keyexchange = ikev2
ike = aes256-sha256-modp1024!
esp = aes256-sha256-modp1024!
#DPD
dpdaction=restart
dpddelay=300s
dpdtimeout=60s
#Branch Office 2
rightfirewall = yes
rightid = 10.20.0.1
right = 10.20.0.1
rightsubnet = 192.168.20.0/24
#headquarters
leftfirewall = yes
leftid = 10.1.0.1
left = 10.1.0.1
leftsubnet = 192.168.1.0/24
#VoIP - Headquarters and Branch Office 2
conn hq-b2-voip
also=hq-b2
leftsubnet = 192.168.3.0/24
rightsubnet = 192.168.23.0/24
#Servers/Headquarters and Users/Branch Office 2
conn hq-b2-servers
also=hq-b2
leftsubnet = 192.168.5.0/24
rightsubnet = 192.168.22.0/24
#VoIP/Branch Office 2 - Headquarters - VoIP/Branch Office 1
conn b2-hq-b1-voip
also=hq-b2
rightsubnet = 192.168.23.0/24
leftsubnet = 192.168.13.0/24Configurer la clé pré-partagée (PSK)
Nous allons configurer notre PSK (Pre-Shared Key), qui sera utilisée pour authentifier les routeurs des autres sites.
- Modifier le fichier
/etc/ipsec.secrets:
: PSK password_PSK4231- Redémarrer le service
ipsecpour prendre en compte les modifications :
root@host:~# systemctl restart ipsec.serviceSite 2 - Branch Office 1
Passons maintenant à la configuration de la première agence. La configuration est similaire à celle du site principal, car elle implique également la configuration des interfaces réseau et du service strongSwan.
Prérequis
- Installer le paquet strongSwan :
root@host:~# apt update && apt install strongswan- Activer le démarrage automatique de
nftables:
root@host:~# systemctl enable nftables.servicenftables
Comme pour le site principal, la configuration de nftables est ici simplifiée. Aucun filtrage ne sera effectué.
- Modifier le fichier
/etc/nftables.conf:
#!/usr/sbin/nft -f
flush ruleset
table inet filter {
chain input {
type filter hook input priority 0; policy accept;
}
chain forward {
type filter hook forward priority 0; policy accept ;
}
chain output {
type filter hook output priority 0; policy accept;
}
}
#NAT for outgoing traffic.
table ip my_nat {
chain my_masquerade {
type nat hook postrouting priority 100;
ip daddr != { 10.10.0.1, 192.168.0.0/16 } oifname wan masquerade comment "output nat"
}
}- Recharger la configuration de
nftables:
root@host:~# nft -f /etc/nftables.confConfiguration Réseau
Configurer les Interfaces Réseau
Nous configurons nos deux interfaces : lan et wan.
- Modifier le fichier
/etc/network/interfaces:
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# and how to activate them. For more information, see interfaces(5).
source /etc/network/interfaces.d/*
# The loopback network interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# The primary network interface
# This is an autoconfigured IPv6 interface
allow-hotplug wan
iface wan inet static
address 10.10.0.1
netmask 255.255.255.0
gateway 10.10.0.254
allow-hotplug lan
iface lan inet static
address 192.168.10.254
netmask 255.255.255.0
up /usr/local/sbin/ipconf.shScript Réseau
Le script /usr/local/sbin/ipconf.sh sera exécuté au démarrage. Il est utilisé pour configurer les interfaces VLAN.
- Créer un fichier
/usr/local/sbin/ipconf.sh:
#!/bin/sh
#SETTING UP VLANs ON THE lan INTERFACE
modprobe 8021q
ip link add link lan name users type vlan id 2
ip link add link lan name voip type vlan id 3
ip link add link lan name wifi type vlan id 4
ip link set users up
ip link set voip up
ip link set wifi up
#VLAN INTERFACE IP ADDRESS SETTINGS
ip addr add 192.168.12.254/24 dev users
ip addr add 192.168.13.254/24 dev voip
ip addr add 192.168.14.254/22 dev wifi
#ENABLE ROUTING
sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward=1- Modifier les droits pour que le script
/usr/local/sbin/ipconf.shsoit exécutable :
root@host:~# chmod +x /usr/local/sbin/ipconf.shstrongSwan
ipsec.conf
- Éditer le fichier de configuration
/etc/ipsec.conf:
#####################################
#Branch Office 1 to Headquarters setup#
#####################################
conn b1-hq
authby = secret
auto = route
type = tunnel
keyexchange = ikev2
ike = aes128-sha1-modp1024!
esp = aes128-sha1-modp1024!
#DPD
dpdaction=restart
dpddelay=300s
dpdtimeout=60s
#Branch Office 1
leftfirewall = yes
left = 10.10.0.1
leftid = 10.10.0.1
leftsubnet = 192.168.10.0/24
#headquarters
rightfirewall = yes
rightid = 10.1.0.1
right = 10.1.0.1
rightsubnet = 192.168.1.0/24
#VoIP - Branch Office 1 and Headquarters
conn b1-hq-voip
also=b1-hq
leftsubnet = 192.168.13.0/24
rightsubnet = 192.168.3.0/24
#Users/Branch Office 1 and Servers/Headquarters
conn b1-hq-servers
also=b1-hq
leftsubnet = 192.168.12.0/24
rightsubnet = 192.168.5.0/24
#VoIP/Branch Office 1 - Headquarters - VoIP/Branch Office 2
conn b1-hq-b2-voip
also=b1-hq
leftsubnet = 192.168.13.0/24
rightsubnet = 192.168.23.0/24Configurer la clé pré-partagée (PSK)
Nous utiliserons la même PSK (Pre-Shared Key) que pour le site principal.
- Modifier le fichier
/etc/ipsec.secrets:
: PSK password_PSK4231- Redémarrer le service
ipsecpour prendre en compte les modifications :
root@host:~# systemctl restart ipsec.serviceSite 3 - Branch Office 2
Prérequis
- Installer le paquet strongSwan :
root@host:~# apt update && apt install strongswan- Activer le démarrage automatique de
nftables:
root@host:~# systemctl enable nftables.servicenftables.conf
- Modifier le fichier
/etc/nftables:
#!/usr/sbin/nft -f
flush ruleset
table inet filter {
chain input {
type filter hook input priority 0; policy accept;
}
chain forward {
type filter hook forward priority 0; policy accept ;
}
chain output {
type filter hook output priority 0; policy accept;
}
}
#NAT for outgoing traffic.
table ip my_nat {
chain my_masquerade {
type nat hook postrouting priority 100;
ip daddr != { 10.20.0.1, 192.168.0.0/16 } oifname wan masquerade comment "output nat"
}
}- Recharger la configuration de
nftables:
root@host:~# nft -f /etc/nftables.confConfiguration Réseau
Configurer les Interfaces Réseau
Ici encore, nous configurons nos deux interfaces (lan et wan).
- Modifier le fichier
/etc/network/interfaces:
# This file describes the network interfaces available on your system
# and how to activate them. For more information, see interfaces(5).
source /etc/network/interfaces.d/*
# The loopback network interface
auto lo
iface lo inet loopback
# The primary network interface
allow-hotplug wan
iface wan inet static
address 10.20.0.1
netmask 255.255.255.0
allow-hotplug lan
iface lan inet static
address 192.168.21.254
netmask 255.255.255.0
up /usr/local/sbin/ipconf.shScript Réseau
Le script /usr/local/sbin/ipconf.sh sera exécuté au démarrage. Il est utilisé pour configurer les interfaces VLAN.
- Créer un fichier
/usr/local/sbin/ipconf.sh:
#!/bin/sh
#SETTING UP VLANs ON THE lan INTERFACE
modprobe 8021q
ip link add link lan name users type vlan id 2
ip link add link lan name voip type vlan id 3
ip link add link lan name wifi type vlan id 4
ip link set users up
ip link set voip up
ip link set wifi up
#VLAN INTERFACE IP ADDRESS SETTINGS
ip addr add 192.168.22.254/24 dev users
ip addr add 192.168.23.254/24 dev voip
ip addr add 192.168.24.254/22 dev wifi
#ENABLE ROUTING
sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward=1- Modifier les droits pour que le script
/usr/local/sbin/ipconf.shsoit exécutable :
root@host:~# chmod +x /usr/local/sbin/ipconf.shstrongSwan
ipsec.conf
- Modifier le fichier
/etc/ipsec.conf:
#####################################
#Branch Office 2 to Headquarters setup#
#####################################
conn b2-hq
authby = secret
auto = route
type = tunnel
keyexchange = ikev2
ike = aes128-sha1-modp1024!
esp = aes128-sha1-modp1024!
#DPD
dpdaction=restart
dpddelay=300s
dpdtimeout=60s
#Branch Office 2
leftfirewall = yes
left = 10.20.0.1
leftid = 10.20.0.1
leftsubnet = 192.168.20.0/24
#headquarters
rightfirewall = yes
rightid = 10.1.0.1
right = 10.1.0.1
rightsubnet = 192.168.1.0/24
#VoIP - Branch Office 2 and Headquarters
conn b2-hq-voip
also=b2-hq
leftsubnet = 192.168.23.0/24
rightsubnet = 192.168.3.0/24
#Users/Branch Office 2 and Servers/Headquarters
conn b2-hq-servers
also=b2-hq
leftsubnet = 192.168.22.0/24
rightsubnet = 192.168.5.0/24
#VoIP/Branch Office 2 - Headquarters - VoIP/Branch Office 1
conn b2-hq-b1-voip
also=b2-hq
leftsubnet = 192.168.23.0/24
rightsubnet = 192.168.13.0/24Configurer la clé pré-partagée (PSK)
Nous utilisons la même PSK (Pre-Shared Key) que pour les autres sites.
- Modifier le fichier
/etc/ipsec.secrets:
: PSK password_PSK4231- Redémarrer le service
ipsecpour prendre en compte les modifications :
root@host:~# systemctl restart ipsec.serviceDépannage
- Ping depuis le Siège :
root@host:~# ping 192.168.21.254 -I 192.168.1.254- Ping depuis Agence 1 :
root@host:~# ping 192.168.5.254 -I 192.168.12.254- Ping depuis Agence 2 :
root@host:~# ping 192.168.13.254 -I 192.168.23.254- Vérifier les logs :
root@host:~# journalctl --grep "ipsec|charon"- Vérifier les connexions IPsec et les associations de sécurité (SA) :
root@host:~# ipsec statusroot@host:~# ipsec statusall