Setting Up Remote Desktop Access on Debian 12 with GNOME
- Last updated: Aug 4, 2024
In a previous tutorial, I demonstrated how to set up a VNC server to establish remote access to a GNU/Linux system. You can find that brilliant guide here. However, with the increasing adoption of Wayland, and the growing complexity of VNC support on it, (see this article: Wayland FAQ), we will explore an alternative solution. In this article, we will look at how to set up an RDP server, which is the native solution for remote desktop access when using GNOME on the latest version of Debian.
⚠️ Please note this limitation: a remote connection can only be established if a session is open. This means we cannot connect to the GDM (GNOME Display Manager).⚠️
Enable Screen Sharing
With GNOME, we have two ways of enabling screen sharing: graphically or via CLI. We will look at both methods.
Graphic Method
- Open Settings:
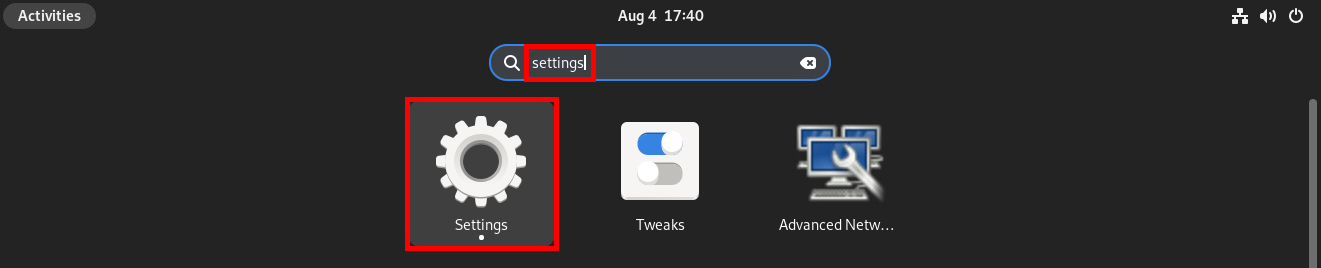
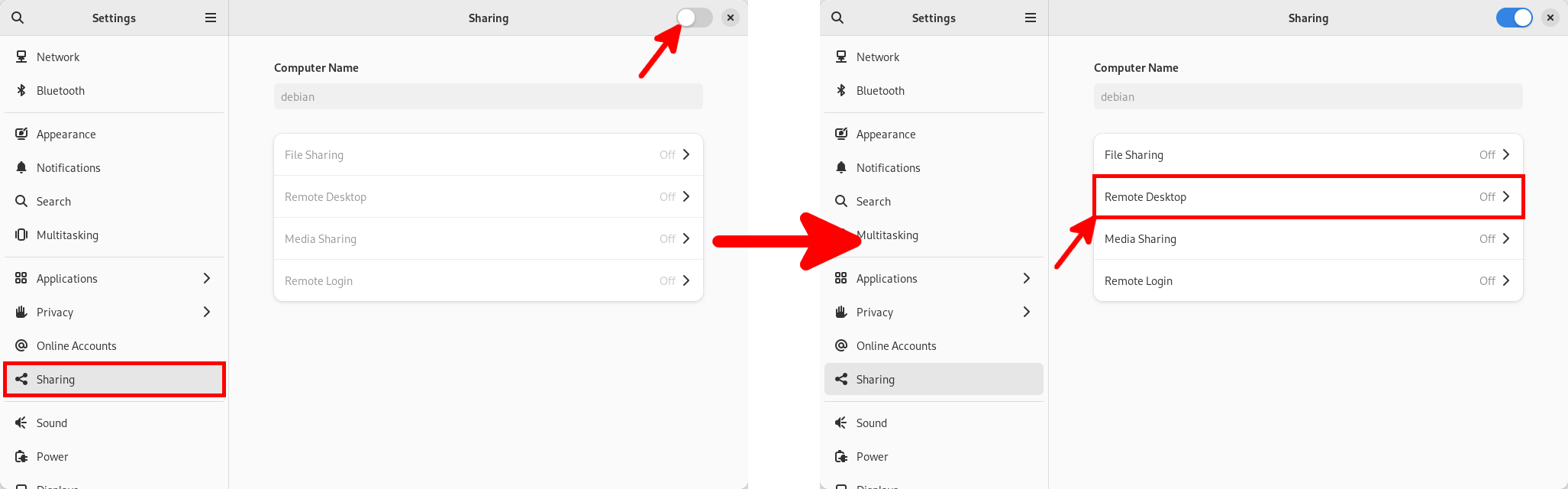
- In Settings, go to Sharing, then move the cursor in the top right-hand corner to the right to activate Sharing. Once enabled, click to Remote Desktop:
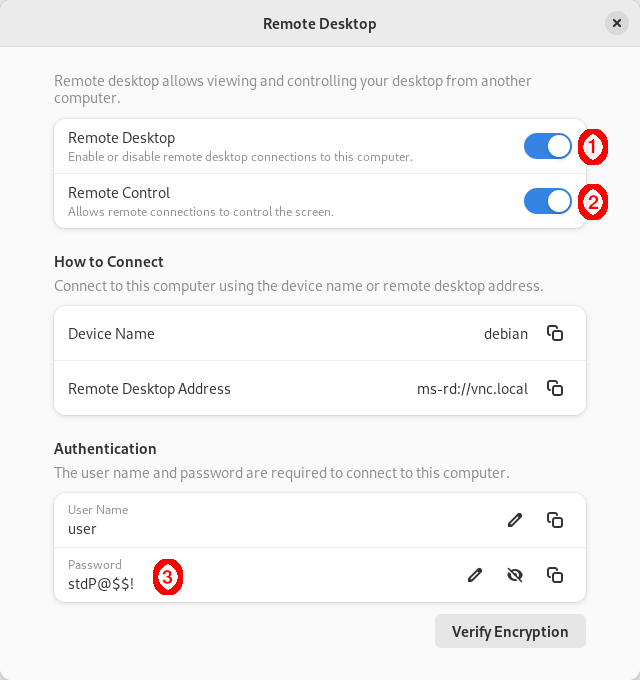
- Enable Remote Desktop (1) with Remote Control (2) and set a Password (3):
CLI Method
It can be useful to enable the remote desktop from CLI. Indeed, if we only have a ssh access to the machine we will be able to enable it. All the configuration will be done with the grdctl tool.
- As a prerequisite, GNOME Remote Desktop must be enabled initially through the GUI. Once activated, it can be disabled or re-enabled with CLI:
- Show the status of the GNOME Remote Desktop service:
user@debian:~$ grdctl status
RDP:
Status: disabled
TLS certificate: /home/user/.local/share/gnome-remote-desktop/rdp-tls.crt
TLS key: /home/user/.local/share/gnome-remote-desktop/rdp-tls.key
View-only: yes
Username: (empty)
Password: (empty)- Set the user and the password:
user@debian:~$ grdctl rdp set-credentials user 'stdP@$$!'- Enable the RDP service:
user@debian:~$ grdctl rdp enable- Enable remote control:
user@debian:~$ grdctl rdp disable-view-only- To disable the RDP service:
user@debian:~$ grdctl rdp disableClient connection
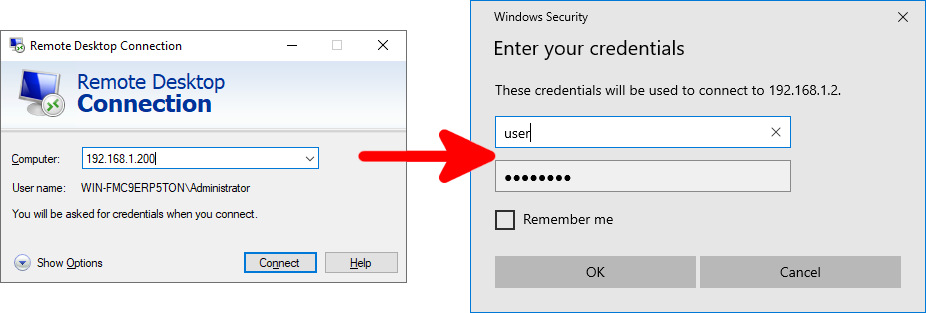
Connect from a Windows host
- Simply open the Remote Desktop Connection client:
Connect from a Linux host

We need to install an RDP client such as FreeRDP. Once installed, we can proceed to connect to the server.
- Install the
freerdp2-waylandpackage:
root@host:~# apt install freerdp2-wayland- Connect to the RDP server:
std@host:~$ wlfreerdp /v:192.168.1.200 /u:"user" /p:'stdP@$$!' /w:1900 /h:1280 /cert:ignore